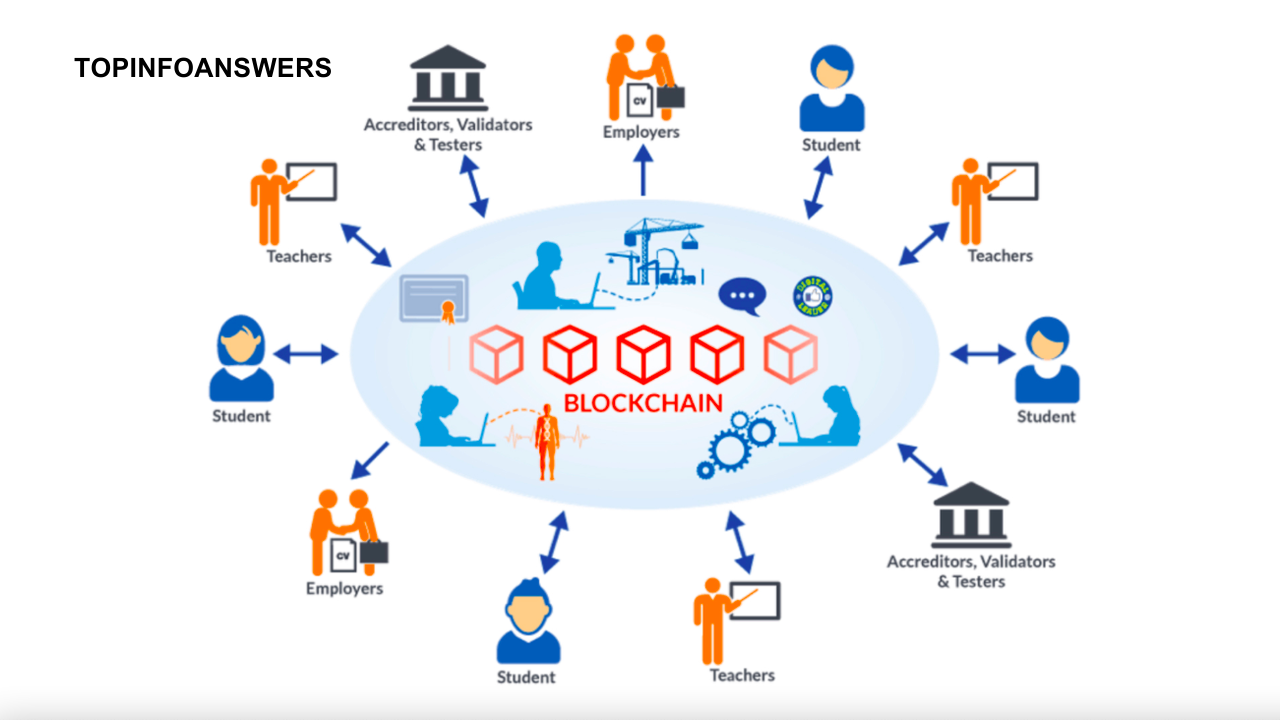
In recent years, blockchain technology has gained widespread attention and is being hailed as one of the most transformative innovations of our time. Initially associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain’s potential far exceeds its original use. One of the most promising applications of blockchain is in the field of education, particularly in credentialing and verification. As educational systems and industries become increasingly globalized, the need for a secure, transparent, and efficient method of verifying academic credentials has never been more critical. Blockchain offers a solution to address these challenges, providing a way to improve the integrity, security, and accessibility of education credentials.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that enables data to be stored across multiple computers in a way that ensures transparency, immutability, and security. Each block in the blockchain contains a list of transactions, and these blocks are linked together in a chain. Once information is recorded on a blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or erase, ensuring the integrity of the data. Because it is decentralized, blockchain removes the need for a central authority, such as a government or institution, to oversee transactions, which fosters trust and transparency.
The Current Challenges in Education Credentialing and Verification
Before diving into how blockchain can improve education credentialing, it’s essential to understand the current challenges faced by educational institutions, employers, and students when it comes to verifying academic credentials.
1. Fraudulent Credentials
Credential fraud is a growing concern worldwide. According to various reports, the global incidence of fake degrees and diplomas is on the rise, with individuals and organizations creating counterfeit certificates to gain employment or admission to prestigious institutions. These fraudulent credentials undermine the credibility of educational systems and can result in the wrong individuals being placed in jobs or programs for which they are not qualified.

2. Manual and Time-Consuming Verification
The traditional process of verifying academic credentials is both time-consuming and cumbersome. It involves contacting the issuing institution, which may be located in a different country, and waiting for confirmation of the authenticity of a degree or diploma. This verification process can take days or even weeks, delaying job offers or admissions decisions. Moreover, educational institutions often have limited resources, making it difficult for them to respond to verification requests in a timely manner.
3. Lack of Standardization
The absence of a standardized system for credentialing across institutions and countries complicates the verification process. Different institutions may have varying formats for diplomas, transcripts, and other credentials, making it difficult for employers or institutions to assess the authenticity and quality of the education that a person has received. Additionally, international students may face challenges in ensuring that their credentials are recognized and valued by institutions or employers in other countries.
4. Limited Access to Credentials
In many cases, students or graduates may face difficulties accessing their own educational credentials. While institutions store students’ records, accessing these records can sometimes be challenging, particularly if a student attended a school that has since closed down or if the institution lacks an efficient digital system for managing credentials. This lack of access can hinder students from applying for jobs or further education, creating unnecessary barriers.
How Blockchain Can Improve Education Credentialing and Verification
Blockchain technology has the potential to address these challenges and revolutionize how educational credentials are issued, verified, and shared. Below are several ways in which blockchain can improve education credentialing and verification.
1. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
One of the most significant advantages of using blockchain in education credentialing is its ability to prevent fraud. Since blockchain records are immutable and transparent, once a credential is issued and added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This creates a tamper-proof record of a student’s academic history that is easily verifiable by employers, institutions, or any other third party.
By storing credentials on a blockchain, educational institutions can eliminate the possibility of fraudulent degrees, diplomas, or transcripts being issued. Blockchain’s encryption ensures that only authorized individuals, such as the student or a verified institution, can update or verify records, further enhancing security.
2. Faster and More Efficient Verification
Blockchain can streamline the credential verification process by providing real-time access to verified educational records. Instead of contacting universities or other educational institutions to verify a degree or diploma, employers or institutions can access the blockchain ledger to confirm a person’s credentials in a matter of minutes. This reduces the time and effort involved in verifying academic qualifications, allowing employers to make hiring decisions faster and institutions to admit students more quickly.
Furthermore, blockchain can automate the verification process using smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts can automatically trigger the verification of academic records when certain conditions are met, such as when an employer requests a candidate’s credentials or when a student applies for a program. This automation not only speeds up the process but also reduces the administrative burden on educational institutions and employers.
3. Standardization of Credentials
Blockchain technology can help create a standardized system for educational credentials, making it easier to assess and compare degrees and qualifications across different institutions and countries. By establishing a common framework for issuing and verifying academic credentials, blockchain can enable better interoperability between educational systems worldwide.
With blockchain, students’ credentials can be represented in a consistent, digital format, making it easier for employers and institutions to evaluate the quality and authenticity of a person’s education, regardless of where they received it. This standardization could help eliminate disparities in how educational qualifications are recognized and valued across borders, facilitating international mobility for students and professionals.
4. Increased Access and Control for Students
Blockchain can give students more control over their academic credentials by allowing them to securely store, access, and share their records at any time. Rather than relying on institutions to provide access to their credentials, students can have a digital wallet that holds their verified academic records on the blockchain. This allows students to share their credentials with potential employers, universities, or other parties without having to go through the traditional verification process.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Education: Benefits and Opportunities
Moreover, blockchain could provide students with greater access to their educational history, even in cases where an institution has closed down or records are otherwise difficult to retrieve. Students would no longer have to rely on outdated or fragile paper-based records, but instead could have access to a secure, digital version of their credentials at any time.
5. Lower Costs for Institutions and Employers
The traditional process of credential verification can be costly for both educational institutions and employers. Institutions often incur administrative costs associated with handling verification requests, while employers may need to dedicate resources to manually verifying candidates’ credentials. By leveraging blockchain, both institutions and employers can reduce these costs significantly.
Since blockchain allows for the automated and real-time verification of credentials, institutions and employers would no longer need to dedicate significant resources to managing the verification process. This would not only reduce costs but also improve efficiency and accuracy, ensuring that the correct information is provided quickly and securely.
6. Facilitating Lifelong Learning and Micro-Credentials
Blockchain can also play a crucial role in facilitating lifelong learning and the recognition of micro-credentials. As the job market evolves and the demand for continuous learning increases, individuals may earn smaller, specialized qualifications throughout their careers. Blockchain allows for the creation of verifiable digital badges, certificates, or other micro-credentials that can be added to a person’s academic record over time.
By providing a secure, verifiable record of micro-credentials, blockchain helps demonstrate an individual’s ongoing professional development and learning, enhancing their employability and ensuring that employers can trust the validity of these qualifications. This could be particularly beneficial in industries where new skills and knowledge are required regularly.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain in Education
Several initiatives and pilot projects have already demonstrated the potential of blockchain for education credentialing and verification. Some notable examples include:
- MIT’s Digital Diplomas: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has implemented a blockchain-based system to issue digital diplomas to graduates. Through the system, graduates can securely share their credentials with employers or other institutions, who can verify them on the blockchain.
- The Learning Machine: This platform allows educational institutions to issue verifiable digital credentials on the blockchain. It is currently being used by several universities and colleges worldwide to create tamper-proof records for their graduates.
- Academic Blockchain Consortium: A group of universities and academic institutions has partnered to explore the use of blockchain technology for managing academic records, aiming to improve verification processes and reduce fraud.
Blockchain has the potential to significantly improve education credentialing and verification, addressing longstanding challenges such as credential fraud, verification delays, and lack of access to records. By leveraging blockchain’s inherent strengths—security, transparency, and decentralization—educational institutions can create more efficient, secure, and accessible systems for issuing and verifying credentials. This not only benefits students by giving them greater control over their academic records but also streamlines processes for employers and institutions, reducing costs and increasing trust in the authenticity of credentials. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, it could reshape the way we think about education and credentialing, making it more secure, transparent, and globally interconnected.