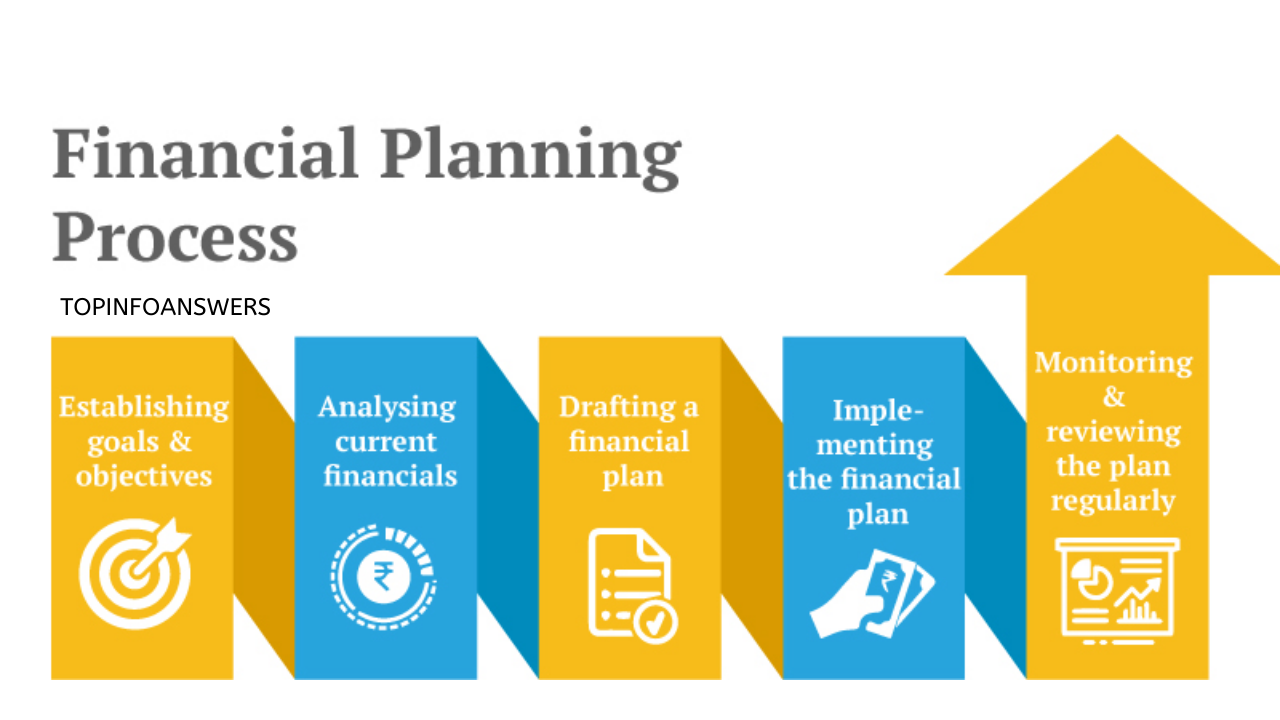
Financial planning is a structured approach to managing your money to achieve specific life goals. Whether you want to buy a house, retire comfortably, start a business, or travel the world, a solid financial plan helps turn your dreams into reality. Without financial planning, it is easy to lose track of income, overspend, and fail to build wealth.
This guide explores the steps to effective financial planning and how you can use it to accomplish your short-term, mid-term, and long-term goals.
Understanding Financial Planning
Financial planning is the process of setting, implementing, and managing financial goals through budgeting, investing, saving, and risk management. It involves evaluating your current financial situation, identifying objectives, and creating a strategic roadmap to reach them.
The Importance of Financial Planning
- Provides Financial Security – Ensures that you have sufficient resources during emergencies and retirement.
- Helps in Wealth Creation – Enables you to invest wisely and grow your assets over time.
- Minimizes Financial Stress – Reduces worries about debts and unplanned expenses.
- Encourages Smart Spending – Helps you prioritize essential expenses and avoid unnecessary spending.
- Prepares for the Future – Ensures you can meet major financial goals such as home ownership, education, and healthcare needs.
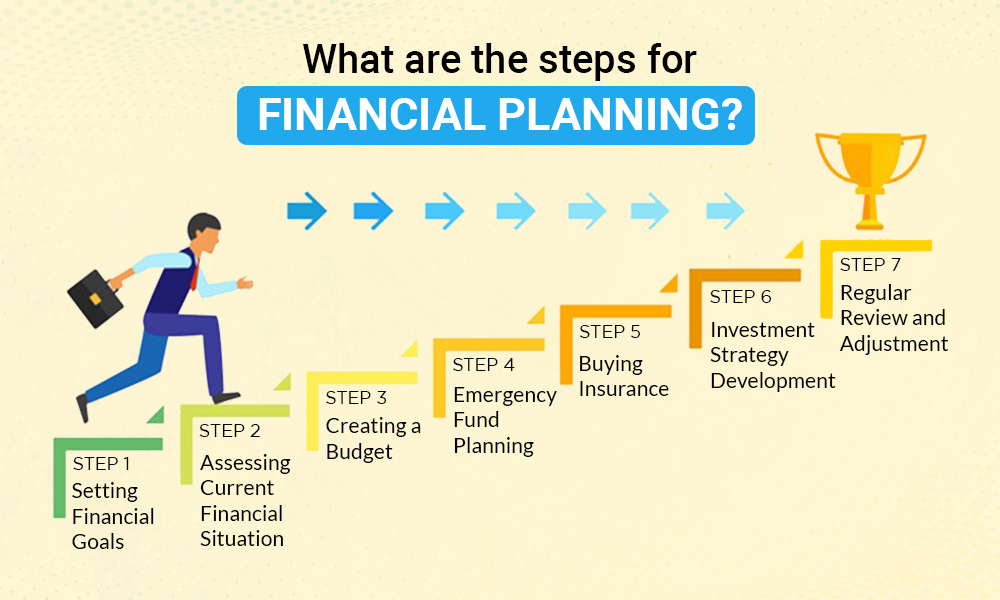
Steps to Effective Financial Planning
1. Set Clear Financial Goals
The first step in financial planning is identifying your life goals and categorizing them based on their time frame.
- Short-term goals (0-3 years): Emergency fund, vacation, buying a car.
- Mid-term goals (3-10 years): Home down payment, higher education, starting a business.
- Long-term goals (10+ years): Retirement, wealth building, financial independence.
Having clear and specific goals ensures that your financial planning efforts remain focused and measurable.
2. Assess Your Current Financial Situation
Before you create a financial plan, analyze your present financial status by evaluating:
- Income: Salary, business profits, rental income, dividends.
- Expenses: Fixed (rent, loans) and variable (entertainment, dining out).
- Debts: Credit cards, student loans, mortgages.
- Assets: Cash, investments, real estate, retirement funds.
- Net worth: Assets minus liabilities.
This assessment provides a realistic understanding of where you stand financially and what adjustments are necessary to reach your goals.
3. Create a Budget
A budget is a fundamental tool for financial planning that helps track income and expenses. Use the 50/30/20 Rule as a basic budgeting strategy:
How to Avoid Financial Pitfalls When Starting a New Business
- 50% for Needs: Rent, groceries, utilities, healthcare.
- 30% for Wants: Entertainment, dining, vacations.
- 20% for Savings & Investments: Retirement, emergency fund, investments.
Maintaining a disciplined budget ensures financial stability and prevents overspending.
4. Build an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a safety net for unexpected expenses like medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent home repairs. Financial planners recommend saving 3 to 6 months’ worth of expenses in an easily accessible account, such as a high-yield savings account.
5. Manage Debt Wisely
Debt can hinder financial progress if not managed effectively. Follow these strategies to reduce and control debt:
- Prioritize high-interest debt: Pay off credit card debts and personal loans first.
- Use the snowball method: Pay off the smallest debts first for motivation.
- Avoid unnecessary borrowing: Stick to essential loans like mortgages and education loans.
- Refinance when possible: Consider lower interest rates to reduce loan burden.

6. Invest for the Future
Investing is essential to wealth creation and financial independence. Consider different investment options based on your risk tolerance and goals:
- Stocks: High potential returns but with risk.
- Bonds: Lower risk with steady income.
- Mutual Funds & ETFs: Diversified and professionally managed.
- Real Estate: Tangible asset with appreciation potential.
- Retirement Accounts (401(k), IRA): Tax-advantaged savings for long-term security.
Diversifying investments reduces risk and enhances long-term returns.
7. Plan for Retirement
Retirement planning ensures a financially secure future. Steps include:
- Start early: The power of compounding grows wealth over time.
- Contribute to retirement accounts: Maximize contributions to employer-sponsored plans and personal retirement accounts.
- Estimate retirement expenses: Consider housing, healthcare, and lifestyle costs.
- Diversify retirement income: Combine pensions, savings, Social Security, and passive income.
8. Protect Yourself with Insurance
Insurance is essential for managing financial risks. Key types include:
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses and prevents financial hardship.
- Life Insurance: Provides financial security for dependents in case of an untimely demise.
- Disability Insurance: Protects income if you cannot work due to illness or injury.
- Home & Auto Insurance: Protects valuable assets from unforeseen damages or accidents.
9. Tax Planning
Effective tax planning helps minimize liabilities and maximize savings. Consider the following:
- Maximize tax deductions: Contributions to retirement funds, health savings accounts, and mortgage interest.
- Utilize tax credits: Education, energy-efficient home improvements, child tax credits.
- Plan capital gains strategically: Hold investments long-term to benefit from lower tax rates.
10. Regularly Review & Adjust Your Financial Plan
Financial planning is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Review and adjust your plan at least once a year or when major life changes occur, such as:

- Job change or salary increase
- Marriage or having children
- Buying a home
- Unexpected expenses or windfalls
This ensures that your financial strategy remains aligned with your goals.
Overcoming Financial Challenges
Achieving financial goals is not always smooth. Common challenges include:
- Lack of Discipline – Avoid impulse spending by sticking to your budget.
- Market Volatility – Stay invested for the long term to weather economic fluctuations.
- Income Instability – Create multiple income streams to safeguard against financial downturns.
- Inflation – Invest in assets that outpace inflation, like stocks and real estate.
Financial planning is a powerful tool that helps you achieve your life goals systematically and efficiently. By setting clear goals, budgeting wisely, investing strategically, and managing risks, you can build financial security and live the life you desire. Start today, stay disciplined, and continuously refine your plan to stay on track toward financial success.