Injuries are a common concern for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and even casual exercisers. Many injuries occur due to inadequate preparation before physical activity. Proper warm-up and stretching routines play a critical role in preventing injuries, improving performance, and promoting overall fitness. This article explores the importance of warm-ups and stretching, the science behind injury prevention, and the best practices to incorporate into your exercise regimen.
Understanding Warm-ups and Stretching
What is a Warm-up?
A warm-up is a preparatory phase before engaging in any strenuous physical activity. It involves low-intensity exercises designed to gradually increase heart rate, blood circulation, and muscle temperature. A proper warm-up helps to activate the nervous system, making muscles more flexible and responsive to physical demands.
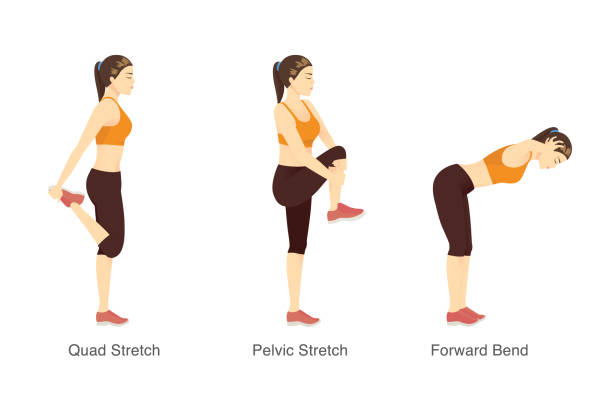
What is Stretching?
Stretching refers to the deliberate elongation of muscles to improve flexibility and range of motion. It is an essential component of injury prevention and muscle recovery. Stretching can be performed as part of a warm-up routine or a cool-down session after exercise.
Importance of Warm-ups in Injury Prevention
1. Increases Blood Flow and Oxygen Supply
Warming up gradually increases heart rate and blood flow to muscles, providing them with essential oxygen and nutrients. This helps reduce muscle stiffness and the risk of strains or tears.
2. Enhances Muscle Flexibility and Joint Mobility
Muscles and joints that are properly warmed up exhibit better flexibility, which reduces the likelihood of injuries. Increased mobility allows for smoother and more efficient movement during exercise.
3. Prepares the Nervous System
A warm-up primes the nervous system, improving coordination and reaction time. This is particularly important in sports and activities requiring quick reflexes and rapid movements.
4. Reduces Muscle Tension and Stiffness
Cold and stiff muscles are more prone to injuries such as sprains and tears. Warming up gradually loosens muscles and tendons, reducing excessive strain during workouts.
5. Improves Performance
A well-prepared body performs better in physical activities. Warm-ups improve overall endurance, strength, and agility, allowing athletes to achieve optimal performance.
Components of an Effective Warm-up
A well-structured warm-up consists of three key components:
1. General Warm-up
This phase includes low-intensity aerobic exercises such as:
- Brisk walking
- Light jogging
- Jumping jacks
- Cycling
These activities elevate heart rate and increase blood circulation, preparing the body for more intense movements.
2. Dynamic Stretching
Unlike static stretching, dynamic stretching involves continuous movement through a range of motion. Some effective dynamic stretches include:
- Leg swings
- Arm circles
- Hip rotations
- High knees
- Lunges with twists
Dynamic stretching warms up muscles while promoting flexibility and coordination.
3. Sport-Specific Movements
For athletes or individuals engaging in specific exercises, incorporating movements that mimic the actual activity is beneficial. For example:
- Basketball players can perform dribbling and shooting drills.
- Runners can do quick strides.
- Weightlifters can perform bodyweight squats or light reps before heavy lifting.
Importance of Stretching in Injury Prevention
1. Enhances Flexibility
Improved flexibility reduces the risk of muscle strains and joint injuries. Flexible muscles can stretch and contract more efficiently, reducing tension and promoting smooth movements.
2. Reduces Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances occur when some muscles are overactive while others are underactive. Stretching helps maintain balanced muscle function, reducing injury risks.
3. Decreases Muscle Soreness
Post-exercise soreness, known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), can be alleviated through stretching. It promotes blood circulation and helps flush out lactic acid buildup in muscles.
4. Improves Posture and Alignment
Regular stretching helps correct posture by loosening tight muscles that contribute to poor alignment. Good posture reduces strain on the spine, neck, and joints.
5. Promotes Relaxation and Stress Relief
Stretching helps reduce stress by relieving muscle tension. This promotes mental relaxation, which is beneficial for overall well-being.
Types of Stretching and Their Benefits
1. Static Stretching
Static stretching involves holding a stretch position for a prolonged period (15-30 seconds). It is best performed after a workout to promote relaxation and recovery. Examples include:
- Hamstring stretches
- Quadriceps stretches
- Shoulder stretches
- Triceps stretches
2. Dynamic Stretching
As mentioned earlier, dynamic stretching involves active movements that improve range of motion. It is most effective as part of a warm-up routine.
3. Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching
PNF stretching involves contracting and relaxing muscles while stretching. It is highly effective for improving flexibility and is commonly used in rehabilitation programs.
4. Ballistic Stretching
Ballistic stretching involves bouncing movements to force a muscle beyond its normal range. While it can increase flexibility, it carries a higher risk of injury and should be done with caution.
5. Active Stretching
In active stretching, you use your own muscle strength to hold a stretch position without external assistance. This method helps improve strength and flexibility simultaneously.
Best Practices for Safe and Effective Stretching

- Warm Up Before Stretching: Stretching cold muscles can lead to injury. Always perform a light warm-up before stretching.
- Stretch Gradually: Avoid jerky movements or forcing a stretch beyond comfort. Stretching should be gradual and controlled.
- Hold Stretches for 15-30 Seconds: This allows muscles to relax and elongate effectively.
- Breathe Deeply: Deep breathing enhances relaxation and increases oxygen flow to muscles.
- Avoid Pain: Stretching should be comfortable. If you feel pain, ease off to prevent injury.
- Be Consistent: Regular stretching yields the best results. Aim for at least 5-10 minutes of stretching daily.
Common Warm-up and Stretching Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping the Warm-up: Jumping into intense exercise without warming up increases injury risks.
- Overstretching Before Exercise: Excessive static stretching before workouts can reduce muscle power and performance.
- Holding Your Breath: Always maintain steady breathing during stretches to maximize effectiveness.
- Bouncing While Stretching: Ballistic stretching can cause muscle tears if not done correctly.
- Ignoring Post-Workout Stretching: Stretching after exercise helps in muscle recovery and reduces soreness.
Proper warm-up and stretching routines are essential for injury prevention, enhanced performance, and overall fitness. A well-structured warm-up prepares the body for physical activity, while stretching improves flexibility and reduces muscle stiffness. By incorporating these practices into your fitness regimen, you can minimize injury risks and optimize your workouts. Prioritize warm-ups and stretching as fundamental components of your exercise routine to ensure long-term health and well-being.