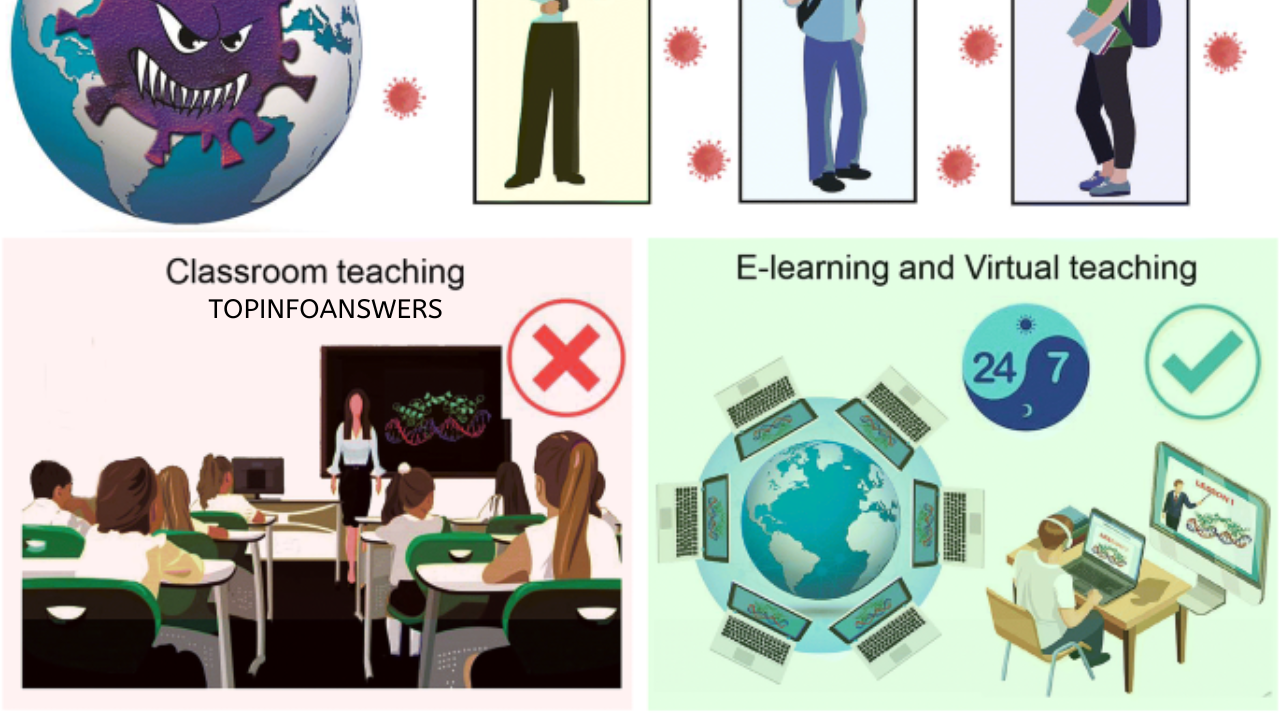
The COVID-19 pandemic brought the world to a standstill, disrupting almost every aspect of daily life. Among the sectors most affected was education. Schools around the world were forced to close their doors to ensure the safety of students and staff. However, learning could not come to a halt. As a result, schools had to rapidly adopt digital learning technologies, leading to a significant transformation in how education is delivered. The pandemic acted as a catalyst for digital learning, accelerating its adoption in ways that were previously unimaginable. This article explores the impact of the pandemic on digital learning in schools, highlighting the changes, challenges, and future prospects of this educational shift.
The Rise of Digital Learning During the Pandemic
1. Transition from Traditional to Online Learning
Before the pandemic, digital learning was gradually being integrated into schools, but the shift was slow and met with resistance. However, with lockdowns and school closures, online learning became the only viable option. Educational institutions had to quickly pivot to virtual classrooms, utilizing video conferencing tools such as Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams to facilitate lessons.

2. Increase in EdTech Solutions
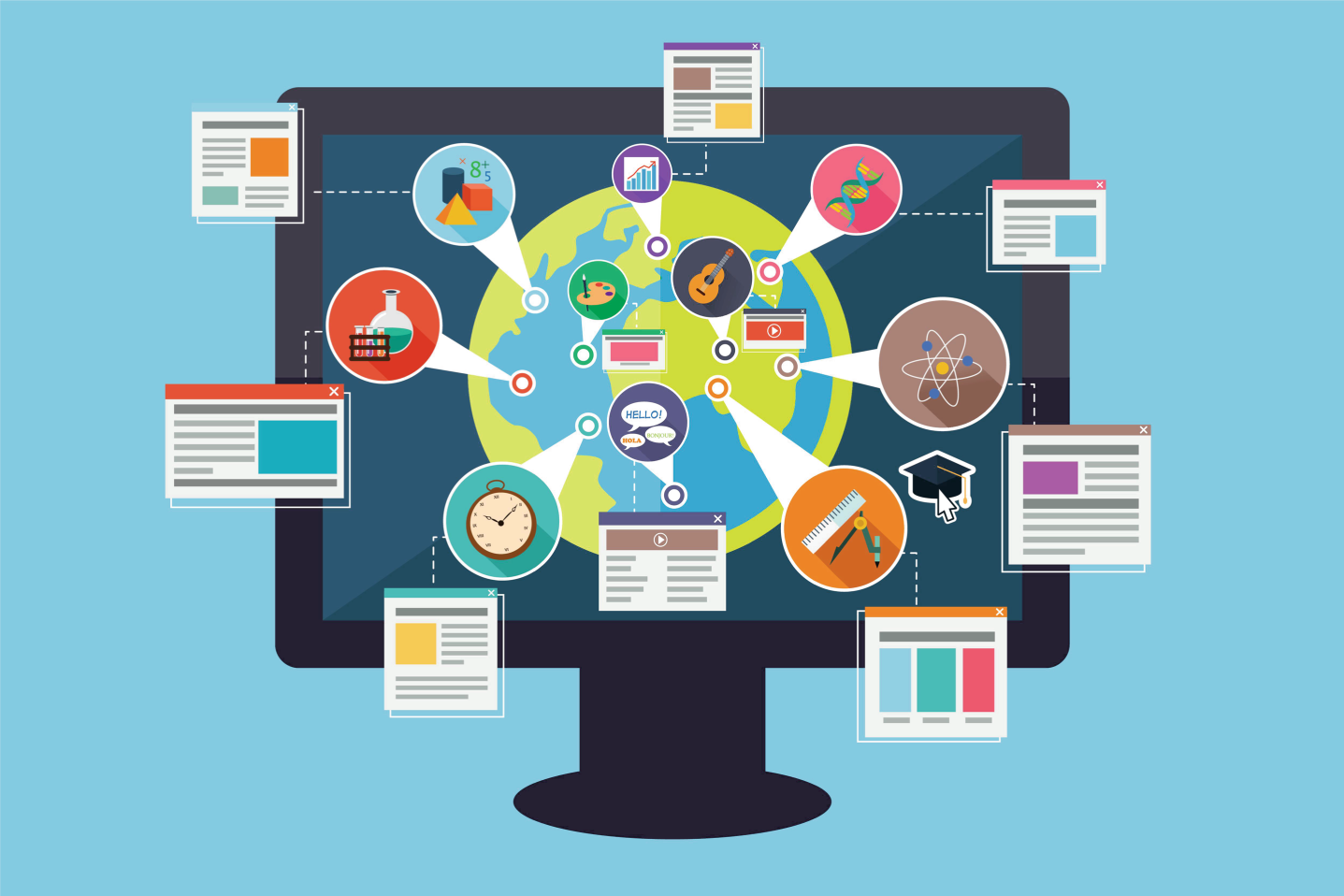
The sudden demand for digital education tools led to the widespread adoption of EdTech solutions. Learning Management Systems (LMS) like Google Classroom, Blackboard, and Moodle saw a surge in usage as schools sought platforms to organize and deliver online coursework. Additionally, AI-driven educational apps, gamified learning platforms, and virtual labs became integral to the learning experience.
3. Digital Content and Resources Expansion
To support remote learning, educational institutions, governments, and private organizations ramped up efforts to create digital learning materials. Open educational resources (OERs) and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) became more prevalent, offering students access to high-quality content from anywhere in the world. Textbooks were converted into digital formats, and many educational institutions collaborated with publishers to make resources more accessible.
Challenges Faced During the Transition
1. Digital Divide
One of the biggest challenges that emerged was the digital divide. Not all students had equal access to the internet or digital devices, making it difficult for them to participate in online learning. Rural areas and underprivileged communities suffered the most, as limited infrastructure and financial constraints made it hard for students to keep up with their peers.
How Schools Can Integrate Social Media for Educational Purposes
2. Teacher Preparedness and Training
Many educators were not adequately trained to use digital tools effectively. While some adapted quickly, others struggled to transition from traditional teaching methods to online instruction. Schools and governments had to invest in teacher training programs to ensure effective delivery of online education.
3. Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Keeping students engaged in a virtual environment proved challenging. Unlike physical classrooms, where teachers could monitor student behavior and engagement levels, online learning required different strategies to maintain interest. Many students found it difficult to concentrate, leading to concerns about the quality of learning outcomes.
4. Cybersecurity and Privacy Concerns
The rapid shift to digital learning also exposed students and teachers to cybersecurity threats. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberbullying incidents increased during this period. Schools had to implement stricter cybersecurity measures to protect student data and maintain a safe online learning environment.
Innovations in Digital Learning Due to the Pandemic
1. Hybrid Learning Models
As schools began reopening, many adopted hybrid learning models that combined in-person and online instruction. This approach allowed for greater flexibility and ensured that students who could not physically attend school due to health concerns could still participate in lessons remotely.
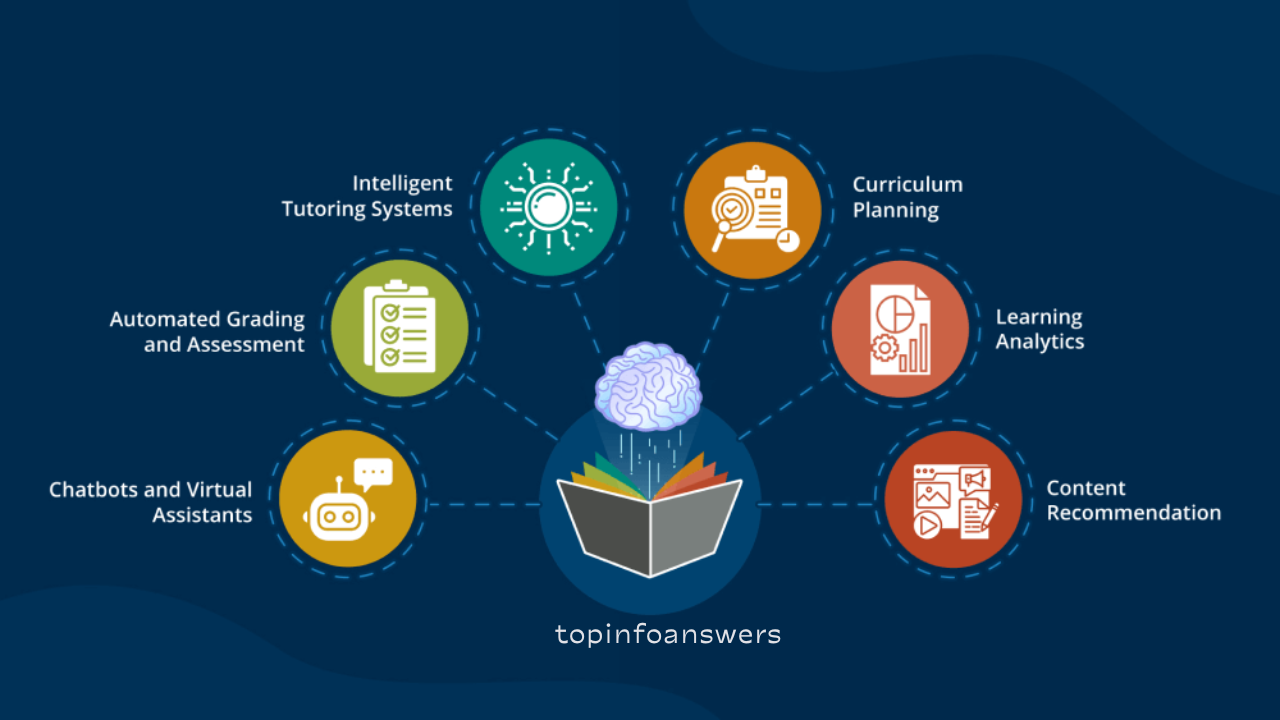
2. AI and Personalized Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) played a significant role in personalizing education. AI-driven platforms analyzed student progress and adapted learning materials based on individual needs. This approach helped bridge learning gaps and provided students with customized support.
3. Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
To enhance digital learning, schools started integrating VR and AR technologies. Virtual field trips, 3D simulations, and interactive learning experiences became more common, making lessons more immersive and engaging for students.
4. Increased Collaboration and Global Learning
The shift to digital learning enabled greater collaboration among schools, teachers, and students worldwide. Virtual exchange programs, international webinars, and online competitions allowed students to connect with peers from different countries, broadening their perspectives and knowledge.
The Future of Digital Learning in Schools
1. Permanent Integration of Technology
Digital learning is no longer an emergency response but a permanent part of the education system. Schools are continuing to invest in technology, digital infrastructure, and teacher training to ensure that online learning remains a viable option.
2. Policy Changes and Government Initiatives
Governments and educational institutions are implementing policies to address issues like the digital divide, cybersecurity, and online curriculum development. Investments in digital education infrastructure, subsidized internet access, and device distribution programs are becoming more common.

3. Blended Learning as the New Norm
The pandemic has demonstrated the effectiveness of blended learning, which combines digital and face-to-face instruction. Many schools are adopting this approach to provide a more flexible and personalized learning experience for students.
4. Expansion of AI and Data Analytics
AI-driven insights and data analytics are expected to play a greater role in shaping education. Schools will use data to track student progress, identify learning gaps, and implement targeted interventions to improve educational outcomes.
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital learning in ways that were previously thought to be years away. While the transition came with its challenges, it also opened new opportunities for innovation and inclusivity in education. As schools continue to integrate digital learning into their curriculums, the future of education is set to be more flexible, personalized, and technology-driven. The lessons learned during this period will shape the education landscape for years to come, ensuring that digital learning remains a fundamental component of modern schooling.