In today’s rapidly changing world, equipping students with the right mindset is just as important as teaching them skills or knowledge. The ability to embrace challenges, learn from failures, and persist in the face of setbacks is a defining trait of successful learners. This mindset, known as a growth mindset, plays a critical role in shaping students’ academic achievements and overall resilience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore effective strategies and practical activities to foster a growth mindset in students, empowering them to become confident, adaptable, and lifelong learners.
2. What Is a Growth Mindset?
Definition and Concept
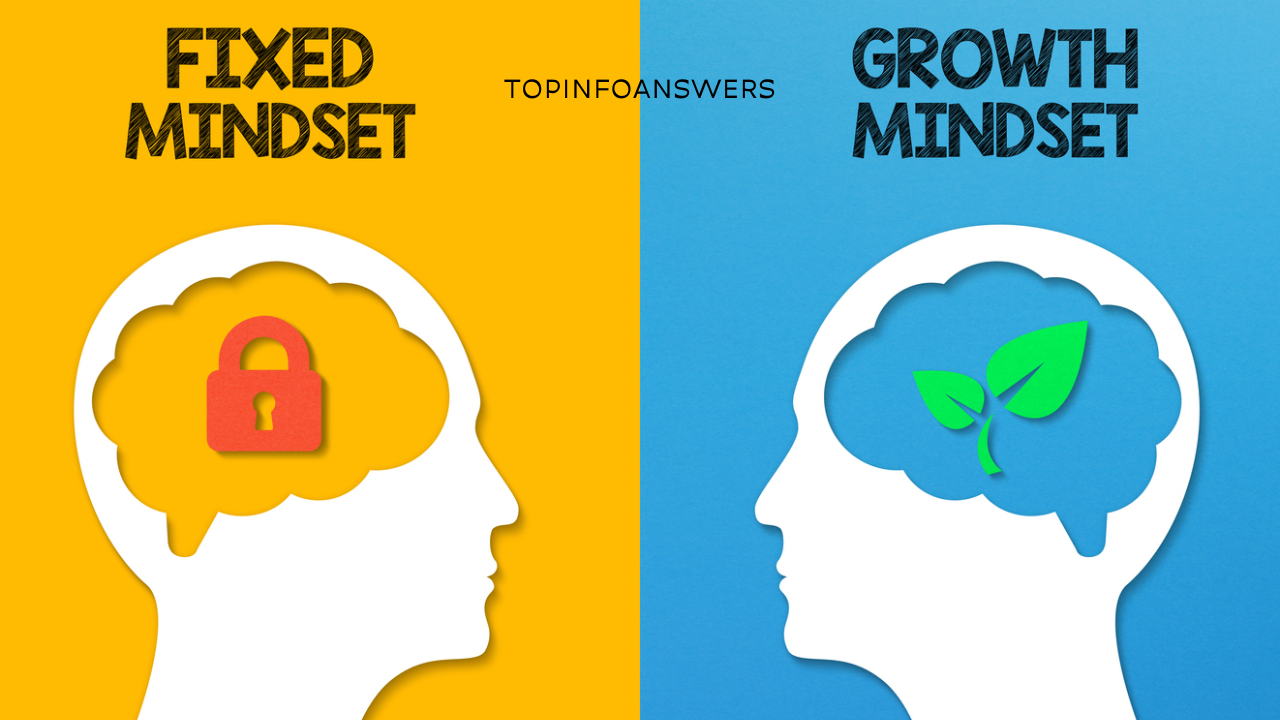
The term growth mindset was coined by psychologist Dr. Carol Dweck in her book Mindset: The New Psychology of Success. It refers to the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort, learning, and perseverance. People with a growth mindset view challenges as opportunities to grow, rather than as limitations of their capabilities.

In contrast, individuals with a fixed mindset believe that their abilities are static traits. They often avoid challenges, fear failure, and perceive effort as fruitless.
Growth Mindset vs. Fixed Mindset
| Growth Mindset | Fixed Mindset |
|---|---|
| Embraces challenges | Avoids challenges |
| Learns from criticism | Ignores or resents criticism |
| Values effort as a path to mastery | Believes effort is useless |
| Inspired by the success of others | Feels threatened by others’ success |
| Views failures as learning opportunities | Views failures as personal flaws |
3. The Importance of a Growth Mindset in Education
Fostering a growth mindset in students offers numerous benefits, including:
✅ Enhanced Academic Performance: Students with a growth mindset are more likely to persevere through difficult tasks and achieve higher academic outcomes.
✅ Resilience and Adaptability: When students view failures as part of the learning process, they become more resilient and adaptable in the face of challenges.
✅ Increased Motivation and Engagement: A growth mindset encourages students to take initiative, ask questions, and engage more actively in the learning process.
✅ Improved Problem-Solving Skills: Students with a growth mindset are more likely to experiment with different strategies and learn from trial and error.
✅ Greater Self-Confidence: Believing in their ability to improve makes students feel more confident and capable.
4. Strategies for Fostering a Growth Mindset in Students
✅ 1. Encourage Effort and Persistence
- Focus on the Process: Praise students for their hard work, dedication, and persistence rather than their innate abilities.
- Model Perseverance: Share personal stories of how you overcame difficulties through continuous effort.
- Normalize Struggle: Reinforce the idea that learning is challenging, and making mistakes is a natural part of the process.
How to Create an Effective Digital Literacy Curriculum: A Comprehensive Guide
✅ 2. Promote the Power of Yet
Introduce the concept of “yet” when students express frustration with their abilities.
- Instead of saying, “I can’t do this,” encourage them to say, “I can’t do this yet.”
- This subtle shift in language helps students see their abilities as a work in progress.
- Create a “Yet Wall” in your classroom where students post their current struggles and the goals they are working towards.
✅ 3. Use Constructive Feedback
- Offer specific and actionable feedback that focuses on strategies and effort rather than personal traits.
- Use growth-oriented language, such as:
- “You’re improving because you kept practicing.”
- “I can see you’re using new strategies to solve this problem.”
- Encourage peer feedback to help students learn from each other’s experiences.
✅ 4. Celebrate Mistakes as Learning Opportunities
- Normalize mistakes by discussing them openly in class.
- Share stories of famous failures (e.g., Thomas Edison, J.K. Rowling) to show that setbacks are stepping stones to success.
- Create a “Favorite Mistake” activity where students share a mistake they learned from.
✅ 5. Teach Goal-Setting and Self-Reflection
- Encourage students to set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Promote regular self-reflection activities, such as journaling about their learning experiences and challenges.
- Use reflection questions like:
- What did I find difficult today?
- How did I overcome a challenge?
- What will I do differently next time?
✅ 6. Encourage Risk-Taking and Resilience
- Create a classroom culture where students feel safe to take risks without fear of ridicule.
- Use activities that require creative thinking and experimentation.
- Teach students that failures are not a reflection of their worth but opportunities for growth.
5. Practical Classroom Activities to Cultivate a Growth Mindset
📌 1. The “Yet” Board
Create a classroom board labeled “The Power of Yet” where students post skills they are still developing.

- Example:
- “I can’t solve complex fractions yet.”
- “I haven’t mastered essay writing yet.”
- This visual reminder helps students embrace ongoing growth.
📌 2. Growth Mindset Journals
Ask students to maintain growth mindset journals where they:
- Write about challenges they faced and how they responded.
- Reflect on progress made over time.
- Identify areas they want to improve.
📌 3. Praise the Process, Not the Person
- Use praise that emphasizes effort, strategies, and determination.
- Instead of saying, “You’re so smart,” say, “I admire how you kept trying different approaches.”
📌 4. Problem-Solving Challenges
- Introduce open-ended problem-solving activities where students collaborate and experiment.
- Highlight that there are multiple solutions and encourage creative thinking.
📌 5. Inspirational Stories of Growth
- Share real-life success stories of individuals who achieved greatness through hard work.
- Encourage students to research and present their own examples of people with growth mindsets.
6. Role of Teachers and Parents in Supporting a Growth Mindset
Teachers’ Role
- Model a growth mindset by sharing your own learning experiences.
- Use inclusive language that promotes learning from mistakes.
- Provide opportunities for students to revise their work and reflect on improvements.
Parents’ Role
- Encourage parents to use growth-oriented praise at home.
- Share resources on fostering a growth mindset with parents.
- Encourage open discussions about challenges and how they lead to growth.
7. Overcoming Challenges in Building a Growth Mindset

- Student Resistance: Some students may struggle to adopt a growth mindset, especially if they have deeply ingrained fixed beliefs. Use gradual reinforcement and consistent encouragement.
- Impatience with Progress: Students may become frustrated if they don’t see immediate improvements. Teach patience and the value of incremental growth.
- External Pressures: High-stakes testing and grading systems may discourage risk-taking. Counteract this by promoting learning for mastery rather than grades alone.
8. Measuring the Impact of a Growth Mindset on Student Performance
- Use self-assessment surveys to measure students’ perceptions of their mindset.
- Track changes in academic performance, participation, and willingness to tackle challenges.
- Collect feedback from students and parents to evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies.
Fostering a growth mindset in students is a transformative process that requires consistent effort, patience, and encouragement. By promoting resilience, embracing mistakes, and valuing the learning journey, teachers and parents can empower students to reach their full potential.
A growth mindset not only improves academic performance but also instills essential life skills such as perseverance, adaptability, and self-confidence, preparing students for future success.
By applying the strategies outlined in this guide, you can create an environment where students thrive on challenges and embrace lifelong learning.