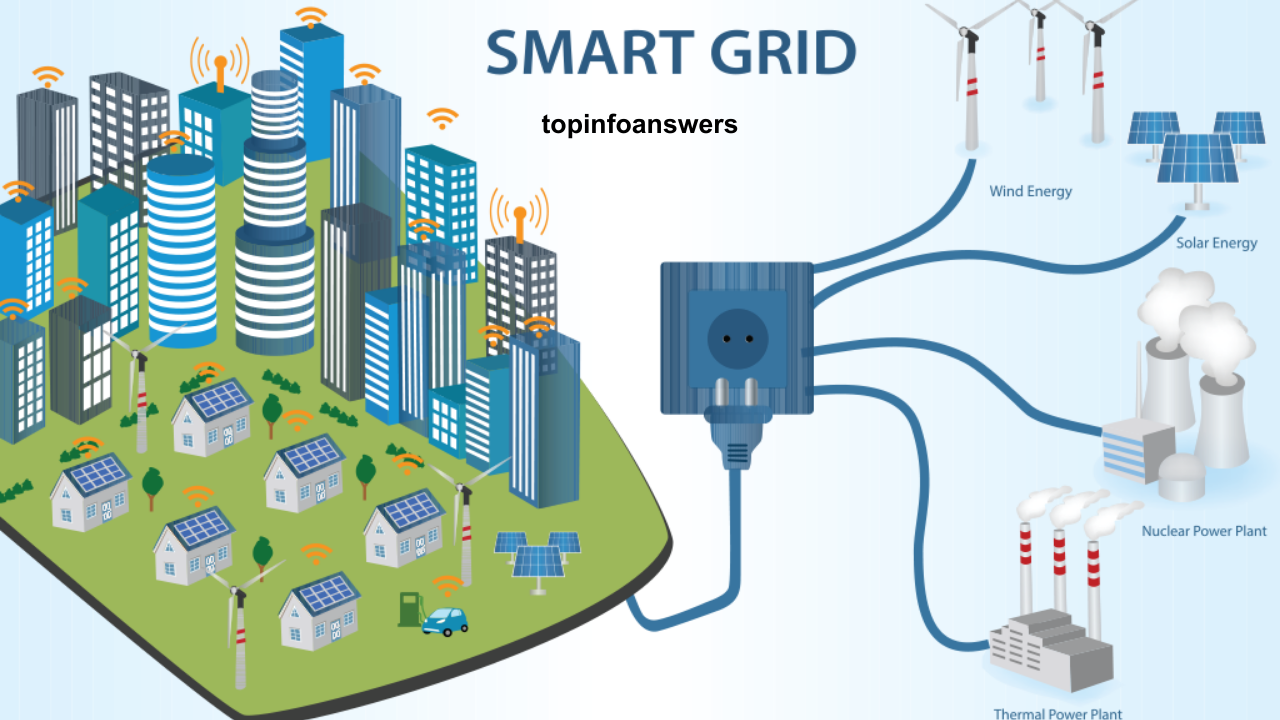
The global energy landscape is undergoing a major transformation as the world shifts towards more sustainable and efficient energy systems. One of the most important innovations in this transformation is the development of smart grids, which play a crucial role in reducing energy waste and improving the overall efficiency of power distribution. A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses digital communication, automation, and data analytics to manage the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity more efficiently. By leveraging technology, smart grids help optimize energy usage, minimize waste, and reduce the environmental impact of energy production and consumption.
Understanding Smart Grids
A traditional electrical grid is a centralized system that transmits electricity from power plants to consumers through transmission lines, substations, and distribution systems. However, these grids are often inefficient due to various factors, including the lack of real-time data, inflexible infrastructure, and a one-way flow of electricity. Smart grids, on the other hand, are designed to be more flexible, dynamic, and interactive. They incorporate a range of technologies, such as:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Smart meters provide real-time data on electricity usage, enabling consumers and utilities to track and manage consumption more effectively.
- Sensors and Automated Controls: Sensors throughout the grid monitor electrical flow, detect faults, and provide real-time data on grid performance. Automated controls can then take action to reroute electricity or optimize distribution.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Smart grids can integrate renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which are intermittent and decentralized in nature, into the grid more effectively.
- Demand Response Systems: These systems allow utilities to adjust electricity demand based on real-time conditions, such as reducing demand during peak periods or encouraging energy usage during off-peak hours.
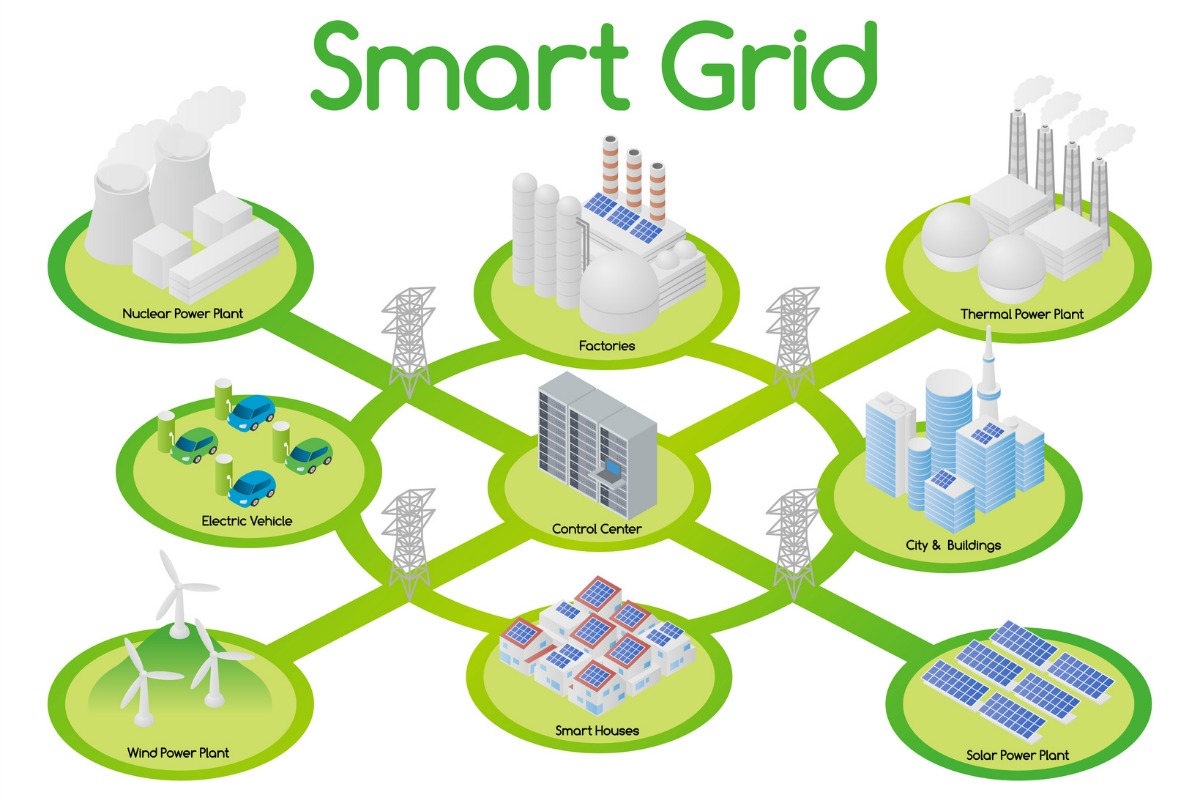
By utilizing these technologies, smart grids provide a more responsive and adaptable system that can help address the growing demand for energy while reducing waste and inefficiency.
How Smart Grids Reduce Energy Waste
The role of smart grids in reducing energy waste is multifaceted. Below are some key ways in which smart grids contribute to more efficient energy use:
1. Optimizing Energy Distribution
One of the main causes of energy waste in traditional grids is the inefficiency of energy distribution. In a conventional grid, electricity often travels long distances from power plants to consumers, resulting in significant losses due to resistance in transmission lines. These losses are typically around 5-7% of the total energy generated, meaning that a significant portion of the energy is wasted before it even reaches consumers.
Smart grids address this issue by optimizing energy distribution in real-time. The integration of sensors and smart meters allows utilities to monitor energy flow across the grid and identify areas where energy is being lost or wasted. Through advanced data analytics, utilities can detect inefficiencies, such as voltage fluctuations or areas with high transmission losses, and take corrective action to optimize energy distribution. This reduces the amount of energy that is lost during transmission, ensuring that more of the generated electricity reaches end consumers.
2. Enabling Demand Response Programs
Demand response is another critical feature of smart grids that helps reduce energy waste. Traditionally, utilities have relied on static pricing models, where consumers pay a fixed price for electricity regardless of when they use it. This often leads to inefficient energy use, as consumers may use electricity during peak demand periods when prices are higher and the grid is under strain. To meet this high demand, utilities may need to activate less efficient, more expensive power plants, resulting in increased energy costs and waste.
How Green Tech is Shaping the Future of the Construction Industry
Smart grids address this problem by enabling dynamic pricing and demand response programs. With real-time data on electricity consumption, utilities can send signals to consumers, encouraging them to reduce or shift their energy use during peak periods. Consumers can respond by adjusting their usage habits, such as turning off non-essential appliances or shifting energy-intensive tasks (like running dishwashers or doing laundry) to off-peak hours. This reduces the need for expensive peak-demand power plants and helps to balance supply and demand more efficiently, thereby reducing energy waste.
3. Improving Energy Storage and Integration of Renewable Energy
Another key advantage of smart grids is their ability to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid more effectively. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent, meaning that their output fluctuates depending on weather conditions. This variability can make it difficult to balance supply and demand, leading to periods of overproduction or underproduction of electricity.
Smart grids help address this challenge by enabling better management of renewable energy through energy storage solutions. For example, during periods of excess renewable energy generation (such as sunny days for solar or windy days for wind energy), smart grids can store excess electricity in batteries or other storage devices for later use. This stored energy can then be used when renewable generation is low, reducing the need for backup fossil fuel-based power plants and minimizing waste.
Additionally, smart grids can facilitate the integration of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as residential solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, into the grid. By enabling two-way communication between consumers and utilities, smart grids allow for the efficient use of locally generated renewable energy, reducing the need for long-distance transmission and minimizing energy losses.
4. Reducing Grid Congestion and Blackouts
Grid congestion occurs when the demand for electricity exceeds the capacity of the grid to deliver it, leading to inefficiencies and potential blackouts. In a traditional grid, congestion is often addressed through the use of reserve power plants, which are typically fossil-fuel-based and less efficient. However, this approach is costly and contributes to environmental pollution.
Smart grids reduce grid congestion by providing real-time data on grid performance and enabling better load balancing. Automated controls can dynamically adjust the flow of electricity, rerouting power to areas that are experiencing high demand or congestion. This helps prevent blackouts and ensures that electricity is distributed more efficiently across the grid. By reducing the need for backup power plants and minimizing congestion, smart grids contribute to a reduction in energy waste and improve the overall reliability of the power grid.
5. Empowering Consumers to Reduce Energy Waste
One of the most significant benefits of smart grids is the ability to empower consumers to take control of their energy consumption. With smart meters and real-time data on energy use, consumers can track their electricity usage patterns and identify areas where they can reduce waste. For example, they may notice that their energy consumption spikes during certain times of day or when certain appliances are in use. By providing this feedback, smart grids enable consumers to make more informed decisions about their energy usage.
The Impact of Sustainable Technologies on the Fashion Industry
In addition to providing data, smart grids often incorporate home energy management systems (HEMS) that allow consumers to automate their energy use. For example, HEMS can automatically turn off lights when rooms are unoccupied, adjust thermostats based on occupancy patterns, or schedule appliances to run during off-peak hours. By enabling consumers to automate and optimize their energy use, smart grids help reduce energy waste at the household level.
6. Reducing Operational and Maintenance Costs
Smart grids also help reduce energy waste by improving the efficiency of grid operations and maintenance. Traditional grids often rely on manual processes to detect faults, maintain equipment, and respond to grid failures. These processes are time-consuming and can lead to delays in addressing issues, which can result in energy losses and wasted resources.
Smart grids, on the other hand, use real-time data to monitor grid performance and detect faults before they lead to significant problems. For example, if a section of the grid experiences a fault or failure, the smart grid can quickly identify the issue and reroute electricity to prevent further disruptions. This proactive approach reduces the need for costly repairs and minimizes downtime, which can result in significant energy savings.
The Environmental Impact of Smart Grids
Reducing energy waste through the implementation of smart grids has a significant positive impact on the environment. By improving the efficiency of electricity distribution and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, smart grids help lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the environmental footprint of energy production. Additionally, by enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, smart grids contribute to the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
How Sustainable Technology is Transforming the Food Industry
Smart grids represent a revolutionary step forward in the way we generate, distribute, and consume electricity. By leveraging advanced technologies such as real-time data, automated controls, and renewable energy integration, smart grids optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and empower consumers to take control of their energy use. As the world continues to move towards more sustainable and efficient energy systems, smart grids will play a critical role in reducing energy waste, lowering costs, and mitigating the environmental impact of energy production and consumption. With ongoing advancements in grid technology and infrastructure, the potential for smart grids to transform the energy landscape is enormous, making them a key component of a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.