In the face of global climate change, one of the most pressing issues is reducing the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is one of the most significant greenhouse gases contributing to global warming. The rising concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has led to an increase in global temperatures, with far-reaching impacts on weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems. As a result, addressing CO2 emissions has become a priority for governments, scientists, and industries worldwide.
Carbon capture technology, also known as carbon capture and storage (CCS), is a critical tool in the fight against climate change. It involves capturing CO2 emissions at their source, transporting them, and storing them underground to prevent their release into the atmosphere. By doing so, carbon capture technology has the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint of industries such as energy production, cement manufacturing, and steel production. In this article, we will explore what carbon capture technology is, how it works, and the potential benefits and challenges associated with its use.
What is Carbon Capture Technology?
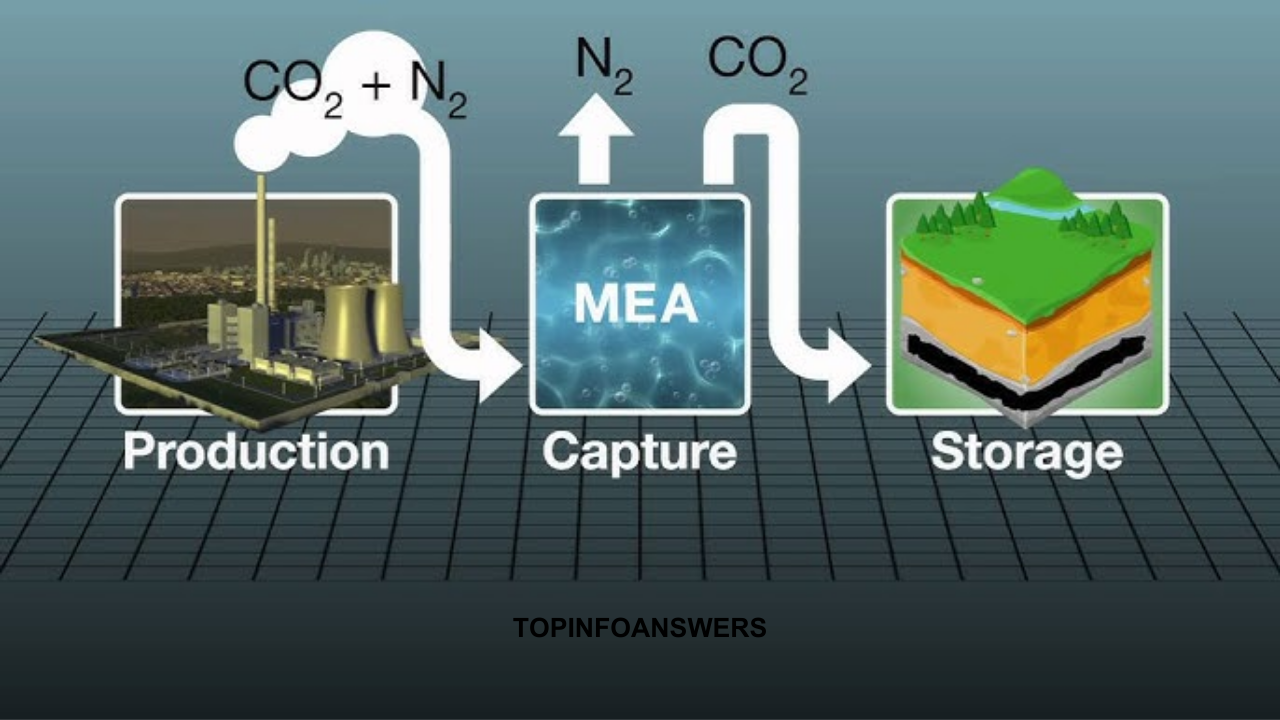
Carbon capture technology refers to a range of technologies designed to capture and store CO2 emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. The process involves three primary steps: capturing CO2 from the source of emission, transporting it to a storage site, and safely storing it underground or in other storage facilities. The captured CO2 can be stored for an extended period, potentially thousands of years, to prevent it from contributing to climate change.

Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is seen as one of the most promising ways to reduce CO2 emissions from industries that are difficult to decarbonize, such as power plants, cement factories, and steel mills. It is particularly valuable in scenarios where it is challenging to reduce emissions through energy efficiency improvements or the use of renewable energy sources. While carbon capture technology is still in the development and scaling-up phase, it is considered a vital component of achieving the global climate targets set by the Paris Agreement and other international efforts.
How Does Carbon Capture Technology Work?
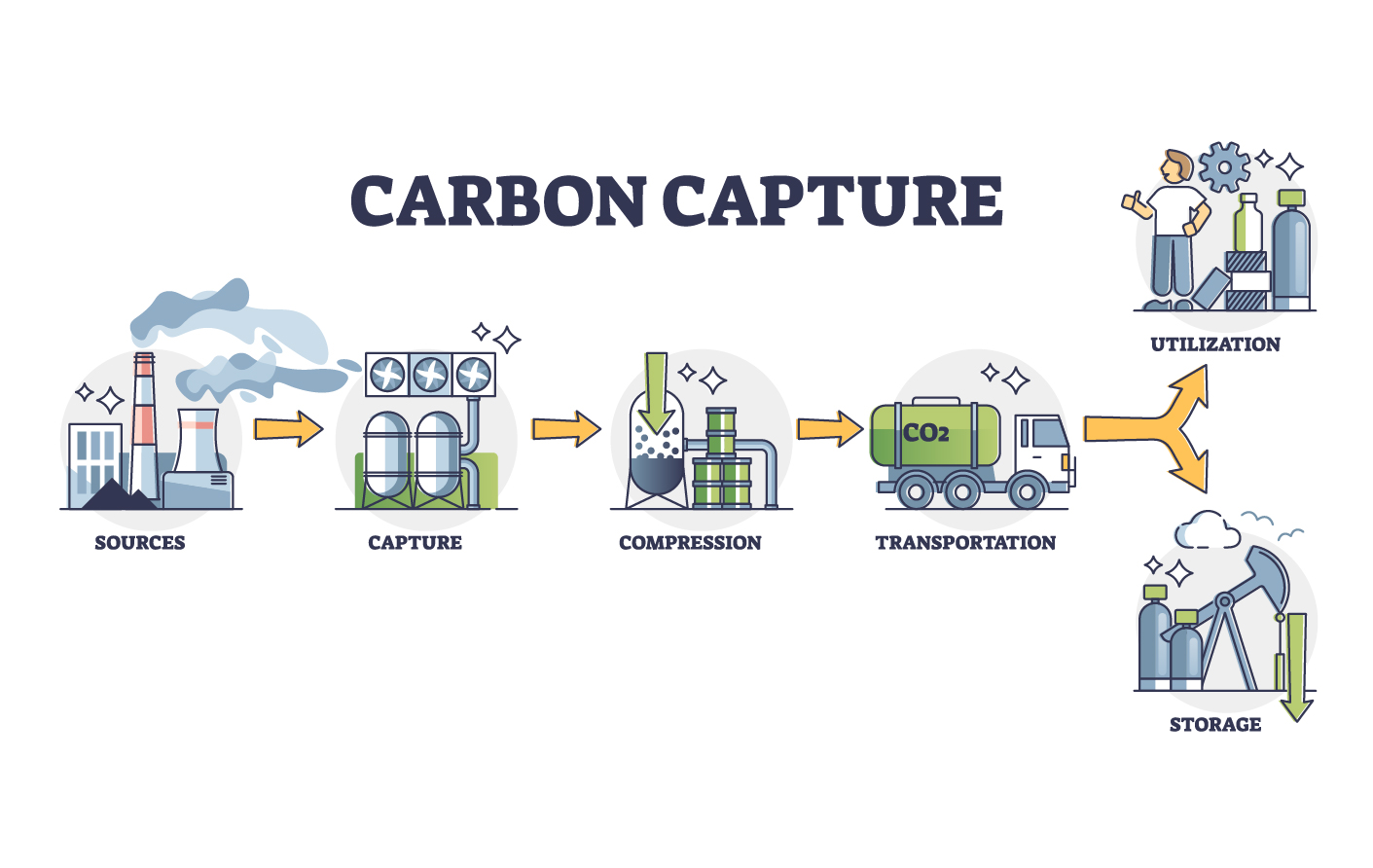
The process of carbon capture can be broken down into three main stages: capture, transport, and storage. Each of these stages plays a critical role in ensuring that CO2 emissions are effectively removed from the atmosphere and stored safely for the long term.
1. Carbon Capture:
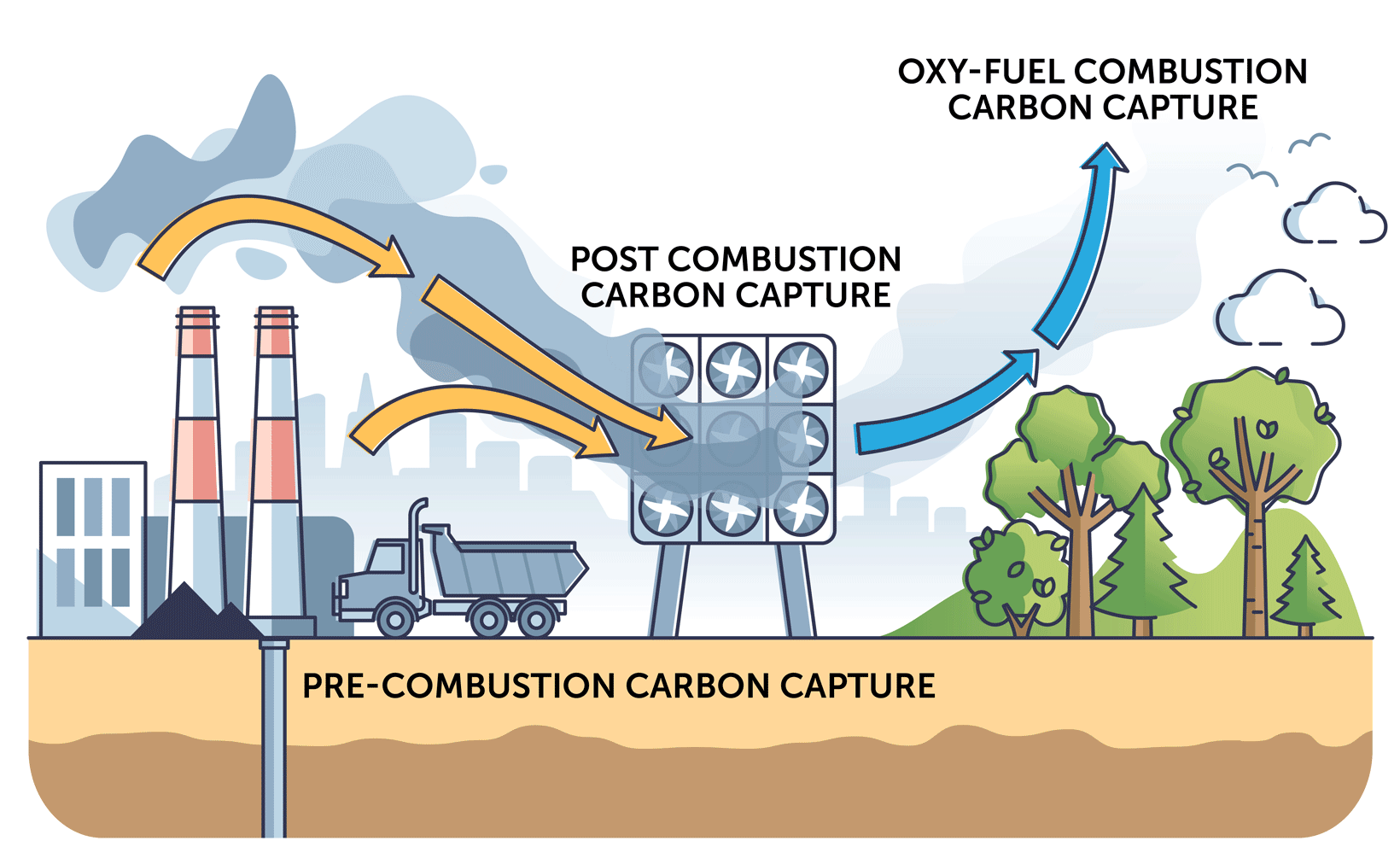
The first step in carbon capture technology is to capture CO2 from industrial sources. CO2 is often emitted from power plants, refineries, factories, and other industrial processes. The capture process can be done in one of three primary ways: pre-combustion capture, post-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion.
- Pre-combustion Capture: In pre-combustion capture, CO2 is removed from fossil fuels before they are burned. This is achieved by converting the fossil fuel into a mixture of hydrogen and CO2 through a process known as gasification. Once the CO2 is separated, the hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel, while the CO2 is captured and sent to storage. This process is commonly used in industries such as steel manufacturing, where the conversion of fossil fuels into hydrogen is more feasible.
- Post-combustion Capture: Post-combustion capture is the most common method of capturing CO2 from flue gases after combustion has already occurred. In this process, the flue gas, which contains CO2, is passed through a solvent that absorbs the CO2. The CO2-rich solvent is then heated to release the captured CO2, which is compressed and transported to storage. This technology is widely used in power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas.
- Oxy-fuel Combustion: Oxy-fuel combustion involves burning fossil fuels in pure oxygen instead of air. This results in a flue gas that is primarily composed of CO2 and water vapor. The water vapor can be condensed and removed, leaving behind a concentrated stream of CO2 that can be captured and stored. Oxy-fuel combustion is considered a promising method for capturing CO2, but it requires specialized equipment and can be energy-intensive.
2. Transporting the Captured CO2:
Once CO2 is captured from the industrial process, it must be transported to a suitable storage location. Transporting CO2 is typically done via pipelines, although it can also be transported by ships or trucks in some cases. Pipelines are the most common method for long-distance transportation, as they are cost-effective and efficient.
CO2 pipelines are typically constructed with high-pressure systems to keep the CO2 in a supercritical state, where it behaves like both a gas and a liquid. This allows for the efficient transportation of large volumes of CO2 over long distances. The pipeline network is carefully designed to minimize leaks and ensure the safe delivery of CO2 to storage sites.
For regions without existing pipeline infrastructure, CO2 can be transported by ship or truck. Shipping is particularly useful for offshore storage locations, such as those located beneath the ocean floor. While trucking is less common, it can be used for smaller-scale CO2 transport over shorter distances.
3. Storing the Captured CO2:
The final stage in carbon capture technology is storing the captured CO2. There are several methods of CO2 storage, but the most common and widely accepted method is geological storage. This involves injecting the CO2 deep underground into geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, deep saline aquifers, or unmineable coal seams.
- Depleted Oil and Gas Reservoirs: Depleted oil and gas reservoirs are among the most promising storage sites for CO2. These are underground formations that have previously been used for oil and gas extraction but are now empty. These reservoirs have been sealed over millions of years, making them ideal for storing CO2. The CO2 is injected into the reservoir and trapped in the porous rock formations, where it remains for thousands of years.
- Deep Saline Aquifers: Saline aquifers are deep underground formations that contain salty water but are not suitable for water extraction. These aquifers can store large volumes of CO2, as the porous rock layers can absorb and trap the gas. Saline aquifers are considered one of the most abundant storage options, with vast potential for CO2 storage around the world.
- Unmineable Coal Seams: Unmineable coal seams are coal deposits that are too deep or too poor in quality to be mined for energy production. These seams can be used to store CO2, as the CO2 can be absorbed by the coal and help to release methane gas, which can then be captured and used as an energy source. This method of storage is still in the experimental phase but holds promise for future CO2 storage projects.
The storage sites are carefully monitored to ensure that the CO2 remains securely stored and does not leak into the atmosphere. Monitoring techniques include measuring the pressure and temperature of the storage sites, as well as using seismic imaging to detect any movement or leakage of CO2. In addition, regulatory frameworks and safety standards are in place to ensure that CO2 storage does not pose any risks to human health or the environment.
Benefits of Carbon Capture Technology
Carbon capture technology offers several key benefits in the fight against climate change:
- Reducing CO2 Emissions: The primary benefit of carbon capture technology is its ability to reduce CO2 emissions from industrial sources. By capturing and storing CO2, the technology helps prevent the gas from entering the atmosphere, thus reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases.
- Decarbonizing Hard-to-Abate Sectors: Certain industries, such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing, are difficult to decarbonize using renewable energy or energy efficiency measures alone. Carbon capture provides a viable solution for reducing emissions in these sectors.
- Supporting Net-Zero Targets: Many countries and companies have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century. Carbon capture technology is considered essential for reaching these targets, particularly for industries where emissions are difficult to eliminate completely.
- Enhancing Energy Security: By capturing CO2 from power plants and other industrial sources, carbon capture technology allows for the continued use of fossil fuels while reducing their environmental impact. This can help maintain energy security while transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
Challenges of Carbon Capture Technology
Despite its potential, carbon capture technology faces several challenges:
- High Costs: The installation and operation of carbon capture systems are expensive. The cost of capturing, transporting, and storing CO2 can make the technology economically unviable without government incentives or a high carbon price.
- Scalability: While carbon capture technology has been successfully demonstrated at pilot and commercial scale in certain sectors, scaling up the technology to a global level is a significant challenge. This requires substantial investment in infrastructure and technological advancements.
- Storage Risks: Although geological storage is considered safe, there are concerns about the long-term integrity of storage sites. Leaks or unintended releases of CO2 could undermine the effectiveness of carbon capture technology.
- Public Acceptance: The deployment of carbon capture technology, particularly the storage of CO2 underground, may face public opposition. People may be concerned about the safety of CO2 storage sites and the potential environmental impacts.
Carbon capture technology plays a crucial role in addressing the global climate crisis by reducing CO2 emissions from industrial sources. Through the processes of capture, transport, and storage, CO2 can be prevented from entering the atmosphere and contributing to global warming. While carbon capture technology offers significant benefits, including its ability to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors and support net-zero targets, it also faces challenges related to cost, scalability, storage risks, and public acceptance.
As research and development continue, carbon capture technology has the potential to become a vital tool in the global effort to combat climate change. With the right investments, policies, and public support, carbon capture could play a key role in achieving a sustainable and low-carbon future for the planet.