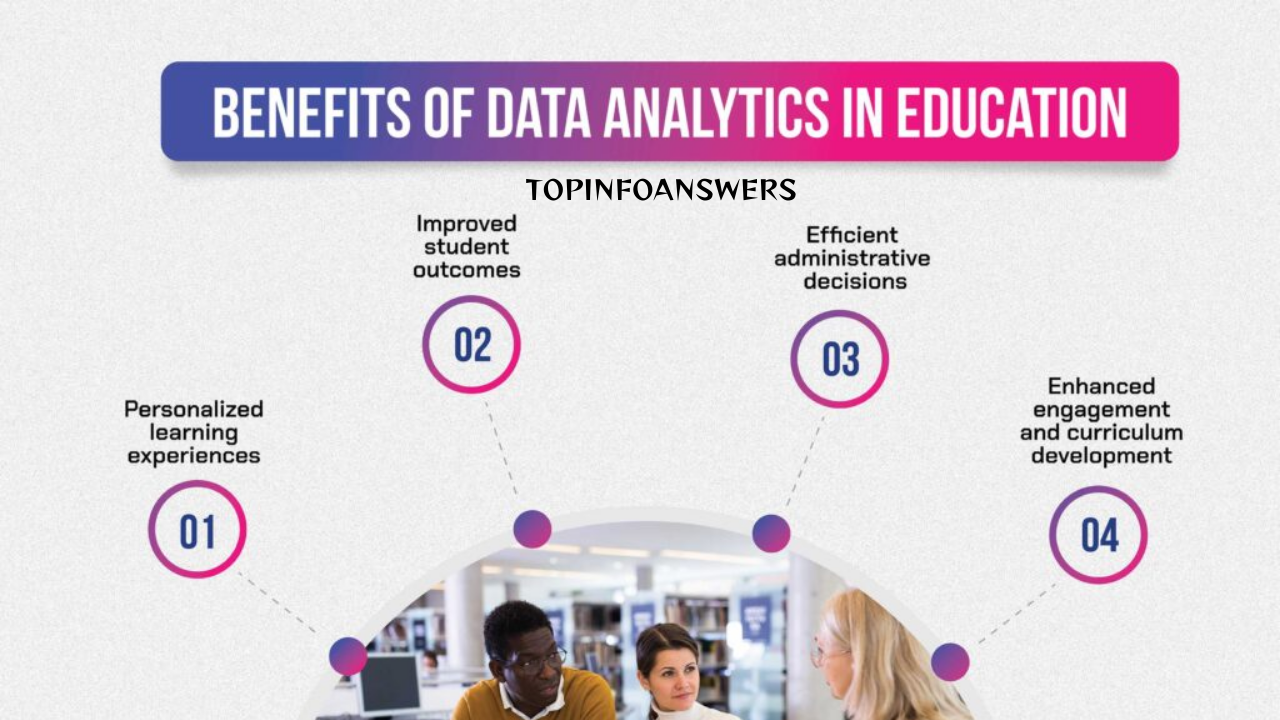
In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, data has become a powerful tool for improving teaching effectiveness. By leveraging data, educators can better understand student learning patterns, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to enhance instructional strategies. This blog post explores the various ways in which data can be utilized to improve teaching effectiveness, the types of data that can be collected, and practical strategies for integrating data-driven decision-making into the classroom.
The Importance of Data in Education
Data-driven teaching is essential for personalizing instruction, measuring progress, and ensuring that every student receives the support they need. The use of data allows educators to:
- Identify student strengths and weaknesses – Assessing students’ performance through data helps teachers understand where students excel and where they need additional support.
- Enhance instructional strategies – By analyzing teaching methods and their outcomes, teachers can modify their approaches for better results.
- Improve student engagement – Data can reveal insights into student motivation and participation, allowing educators to develop strategies to increase engagement.
- Support educational equity – By identifying gaps in achievement among different student groups, data helps address disparities and promote inclusivity.
- Make evidence-based decisions – Teachers can use data to guide curriculum planning, instructional design, and classroom management.
Types of Data in Education
Educators can use various types of data to inform their teaching practices. Some of the most useful types include:
1. Student Performance Data
- Standardized test scores – Provide a broad measure of student proficiency in core subjects.
- Classroom assessments – Include quizzes, tests, and projects that help track student progress.
- Formative assessments – Such as exit tickets, peer reviews, and self-assessments that provide ongoing feedback.
- Summative assessments – Final exams and cumulative projects that evaluate overall learning outcomes.
2. Behavioral Data
- Attendance records – Track student presence in class and identify patterns of absenteeism.
- Disciplinary records – Help understand behavioral challenges and develop interventions.
- Participation rates – Measure student engagement in discussions, group work, and online activities.
The Importance of Teacher Collaboration in Enhancing Student Learning
3. Student Feedback Data
- Surveys and questionnaires – Provide insights into student perceptions of teaching methods, classroom environment, and learning difficulties.
- Course evaluations – Help teachers refine their instructional strategies based on student feedback.
4. Teacher Performance Data
- Peer observations – Offer constructive feedback on teaching practices.
- Student evaluations – Reflect students’ perspectives on instructional effectiveness.
- Self-reflection logs – Encourage teachers to analyze their own strengths and areas for improvement.
5. Classroom and School-Wide Data
- Curriculum effectiveness data – Assesses how well the curriculum aligns with student learning needs.
- Resource utilization – Helps understand the impact of teaching materials, technology, and classroom resources on student learning.
- School-wide trends – Identify overarching trends in student achievement, graduation rates, and learning gaps.
Strategies for Using Data to Improve Teaching Effectiveness
1. Setting Clear Learning Goals
Data allows teachers to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) learning objectives. For example, if data reveals that a majority of students struggle with reading comprehension, a teacher can set a goal to improve comprehension skills through targeted activities.

2. Personalizing Learning
By analyzing student performance data, teachers can tailor instruction to meet individual needs. Strategies include:
- Differentiated instruction – Adjusting content, process, and assessment methods based on student abilities.
- Adaptive learning technology – Using digital tools that provide personalized learning experiences.
- Targeted interventions – Offering additional support through tutoring, peer mentoring, or small-group instruction.
3. Implementing Formative Assessments
Frequent formative assessments help teachers gauge student understanding in real-time and make adjustments as needed. Examples include:
- Exit tickets – Short questions at the end of a lesson to assess comprehension.
- Think-pair-share – Encouraging students to discuss concepts with peers before sharing with the class.
- Online quizzes – Immediate feedback through digital platforms.
4. Using Data to Improve Classroom Management
Behavioral data can inform classroom management strategies. For instance:
- Tracking attendance trends – Identifying students at risk of chronic absenteeism and providing support.
- Analyzing participation patterns – Encouraging shy students to engage more actively.
- Developing positive reinforcement techniques – Rewarding good behavior to promote a constructive learning environment.
5. Enhancing Professional Development
Teachers can use data to refine their instructional techniques and professional growth. This includes:
- Peer collaboration – Sharing best practices with colleagues based on data-driven insights.
- Professional learning communities (PLCs) – Engaging in group discussions to address teaching challenges.
- Continuous self-assessment – Reflecting on teaching methods and student feedback.
6. Leveraging Technology for Data Analysis
Technology plays a crucial role in data-driven education. Tools such as learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), and AI-driven analytics provide real-time insights into student performance. Examples include:
- Google Classroom – Tracks student progress and engagement.
- Khan Academy – Offers adaptive learning experiences based on student data.
- PowerSchool – Manages student records and generates performance reports.
7. Communicating Data Insights with Stakeholders
Effective communication of data findings with students, parents, and administrators fosters collaboration and support. Methods include:
- Parent-teacher conferences – Discussing student progress and strategies for improvement.
- Student data reports – Providing clear and actionable feedback.
- School-wide data meetings – Aligning teaching strategies with school goals.
Challenges in Data-Driven Teaching and How to Overcome Them
1. Data Overload
Too much data can be overwhelming. Solution:
- Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to student learning.
- Use dashboards and visual tools for easy data interpretation.
2. Data Accuracy Issues
Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to misleading conclusions. Solution:
- Ensure proper data collection methods and validation processes.
- Cross-check data from multiple sources.
3. Time Constraints
Analyzing data takes time, which teachers often lack. Solution:
- Use automated data analysis tools.
- Integrate data review into routine lesson planning.
4. Resistance to Change
Some educators may be reluctant to adopt data-driven methods. Solution:
- Provide training on data literacy.
- Demonstrate success stories and positive outcomes.
How to Build a Supportive Learning Community in Online Courses
Data is a powerful ally in improving teaching effectiveness. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and applying data insights, educators can enhance instructional strategies, personalize learning experiences, and foster student success. While challenges exist, they can be mitigated with proper planning, technology integration, and collaboration among stakeholders. Ultimately, a data-driven approach empowers teachers to make informed decisions that positively impact student learning and overall educational outcomes.