Agriculture has been the backbone of human civilization for thousands of years. Over time, farming practices have evolved with technological advancements, improving efficiency and productivity. Today, smart agriculture, also known as precision farming or AgriTech, is revolutionizing the farming industry. By integrating modern technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and big data analytics, farmers can maximize their output while minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact. This blog post explores the concept of smart agriculture, its benefits, technological innovations, and its future potential.
Understanding Smart Agriculture
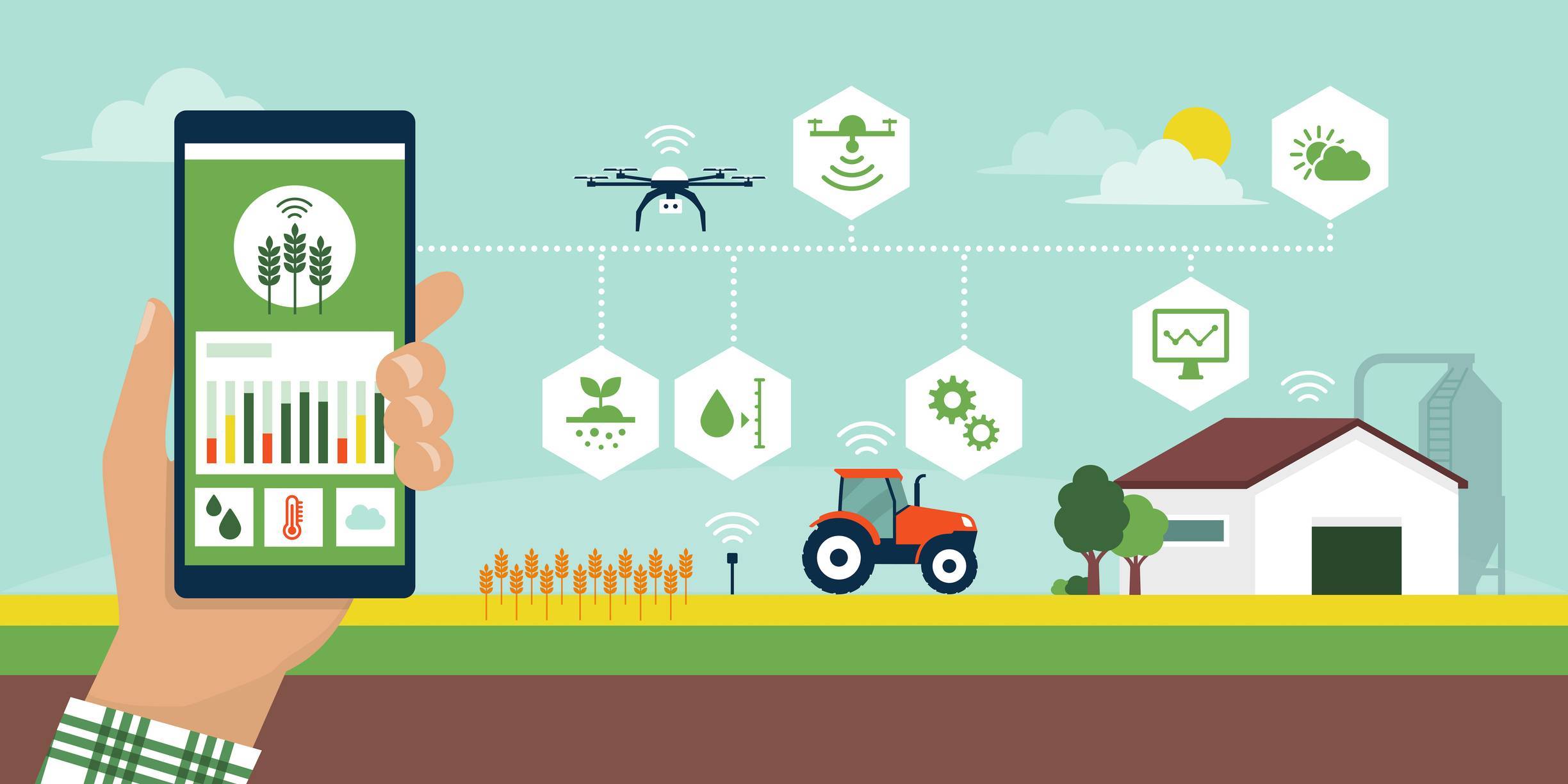
Smart agriculture refers to the application of digital technologies and data-driven solutions to optimize farming processes. Unlike traditional farming, which relies on manual labor and conventional techniques, smart agriculture leverages automation, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Smart agriculture aims to address major challenges in modern farming, such as unpredictable weather patterns, soil degradation, water scarcity, pest infestations, and the increasing demand for food due to global population growth. By adopting smart technologies, farmers can make informed decisions, reduce operational costs, and improve crop yield.
Key Technologies Driving Smart Agriculture
1. Internet of Things (IoT) in Farming
IoT-enabled devices have transformed agriculture by enabling real-time data collection and analysis. Smart sensors and connected devices are used to monitor soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels, allowing farmers to make precise adjustments to their farming practices.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: These systems use IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture and deliver water efficiently, reducing water wastage and ensuring crops receive the optimal amount of hydration.
- Livestock Monitoring: Wearable IoT devices help track the health and movement of livestock, ensuring early disease detection and improving animal welfare.
- Smart Greenhouses: IoT-based greenhouses use automated climate control systems to optimize temperature, humidity, and lighting, maximizing crop production.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML play a crucial role in smart agriculture by analyzing large datasets to provide actionable insights. These technologies help in crop monitoring, disease detection, and predictive analytics.
- AI-Powered Drones: Drones equipped with AI and computer vision can survey large farmland areas, detect pest infestations, assess crop health, and monitor irrigation needs.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models analyze historical and real-time data to forecast weather patterns, crop diseases, and market demand, helping farmers make data-driven decisions.
- Automated Weed and Pest Detection: AI-powered machines can identify and remove weeds or pests without using excessive pesticides, reducing chemical usage and improving sustainability.
3. Big Data and Analytics
Big data is transforming agriculture by enabling farmers to analyze historical trends and current conditions to make informed decisions. By collecting data from IoT devices, satellites, and agricultural management systems, farmers can optimize crop rotation, fertilization, and harvesting schedules.
How Renewable Energy Technologies Are Shaping the Future of Power
- Yield Prediction: By analyzing soil quality, weather conditions, and crop health, big data analytics can predict yields, helping farmers plan better.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Data analytics helps streamline the agricultural supply chain by improving inventory management, reducing food wastage, and predicting market trends.
- Soil Health Monitoring: Sensors collect data on soil composition, pH levels, and moisture content, providing farmers with insights on soil fertility and nutrient deficiencies.
4. Robotics and Automation
Automation is playing a significant role in smart farming by reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. Robotics and automated machinery are used for planting, harvesting, and maintenance.
- Autonomous Tractors: Self-driving tractors use GPS and AI to plow, seed, and fertilize fields with high precision.
- Robotic Harvesters: Advanced robotic systems can harvest fruits and vegetables without damaging them, improving efficiency and reducing labor dependency.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: These systems use AI and IoT to adjust water distribution based on real-time soil and weather data.
5. Blockchain in Agriculture
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in the agricultural supply chain. By recording transactions in a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures food safety, fair trade, and efficient logistics.
- Food Traceability: Consumers can track the journey of agricultural products from farm to table, ensuring quality and authenticity.
- Smart Contracts: Farmers can use blockchain-based smart contracts to automate transactions, reducing fraud and ensuring fair pricing.
- Secure Data Management: Blockchain secures farm data, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
Benefits of Smart Agriculture
The adoption of smart agriculture technologies offers numerous benefits for farmers, consumers, and the environment.
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automation and AI-driven decision-making help farmers optimize resource usage, reduce waste, and increase overall productivity. Precision farming techniques ensure that crops receive the right amount of nutrients, water, and protection, leading to higher yields.
2. Cost Reduction
Smart farming technologies reduce labor costs, minimize fertilizer and pesticide usage, and optimize water consumption. Automated machinery and predictive analytics help farmers allocate resources more efficiently, leading to significant cost savings.
3. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Farming
Smart agriculture promotes sustainable farming practices by reducing chemical use, conserving water, and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Technologies like AI-driven pest control and IoT-based irrigation systems contribute to environmental conservation.
4. Improved Crop Quality and Food Safety
By monitoring soil health, weather conditions, and plant diseases, smart agriculture ensures better crop quality. Blockchain-based traceability systems enhance food safety by providing transparency in the supply chain.
The Impact of Electric Vehicles on Reducing Carbon Emissions
5. Better Risk Management
With predictive analytics and real-time monitoring, farmers can anticipate weather changes, pest outbreaks, and market fluctuations, reducing risks and improving decision-making.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Agriculture
Despite its numerous advantages, smart agriculture faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
1. High Initial Investment
The implementation of smart farming technologies requires significant investment in IoT devices, AI-powered systems, and automated machinery. Small-scale farmers may find it difficult to afford these technologies.
2. Lack of Technical Knowledge
Many farmers lack the necessary technical expertise to operate and maintain smart agricultural systems. Training and education programs are essential to bridge this gap.
3. Connectivity Issues
Smart agriculture relies on internet connectivity for real-time data collection and analysis. Rural areas with poor network infrastructure may struggle to adopt these technologies.
4. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
With increasing digitization, the risk of cyber threats and data breaches also rises. Protecting farm data from unauthorized access is crucial.

The Future of Smart Agriculture
The future of smart agriculture looks promising, with continuous advancements in AI, robotics, and IoT. Some emerging trends that will shape the future of farming include:
- 5G Connectivity: Faster and more reliable internet connectivity will enhance real-time monitoring and automation in agriculture.
- Vertical Farming: Urban and indoor farming solutions using AI-driven climate control systems will revolutionize food production in densely populated areas.
- Gene-Editing Technologies: CRISPR and other genetic modification techniques will help develop disease-resistant and high-yield crops.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Advanced technologies will enable farmers to adapt to climate change, ensuring food security in the face of environmental challenges.
How IoT is Helping in Environmental Monitoring and Protection
Smart agriculture is transforming the way we grow food, making farming more efficient, sustainable, and profitable. With innovations in IoT, AI, robotics, and blockchain, farmers can optimize their practices, reduce costs, and improve food quality. However, challenges such as high costs, technical knowledge gaps, and connectivity issues must be addressed for widespread adoption. As technology continues to evolve, smart agriculture will play a crucial role in feeding the growing global population while preserving natural resources. Investing in AgriTech today will ensure a more resilient and productive agricultural sector for the future.











