Financial independence is the ability to live comfortably and meet financial needs without relying on employment or external financial support. Achieving financial independence requires a combination of disciplined saving, wise investing, and strategic financial planning. Investing smartly ensures that money works for you, growing over time and creating passive income streams. This guide explores the strategies, principles, and approaches to achieve financial independence through smart investing.
Understanding Financial Independence
Financial independence occurs when your investments generate enough passive income to cover your living expenses. This is typically achieved through a combination of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. Key principles of financial independence include:
- Building a Strong Financial Foundation: Minimizing debt, controlling expenses, and increasing savings.
- Investing Wisely: Allocating assets to investments that offer long-term growth and passive income.
- Managing Risk: Diversifying investments and mitigating financial risks.
- Developing Multiple Income Streams: Relying on various income sources such as dividends, rental income, or business profits.
- Long-Term Planning: Setting financial goals and adjusting investments to achieve financial security.

Steps to Achieve Financial Independence Through Smart Investing
1. Setting Clear Financial Goals
Before investing, define clear financial goals that align with your vision of financial independence. Goals can be categorized as:
- Short-term (1-5 years): Building an emergency fund, saving for a down payment.
- Mid-term (5-15 years): Accumulating assets, starting a business, or funding children’s education.
- Long-term (15+ years): Retirement planning, wealth transfer, or philanthropic endeavors.
2. Budgeting and Saving for Investments
Investing requires capital, which is generated through disciplined saving. Follow these steps to ensure an adequate investment fund:
- Track expenses: Identify unnecessary expenses and reduce spending.
- Follow the 50/30/20 rule: Allocate 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings/investments.
- Automate savings: Direct a portion of income into investment accounts.
- Eliminate high-interest debt: Pay off credit cards and loans to free up capital for investing.
3. Understanding Investment Vehicles
A diversified investment portfolio is crucial for long-term financial success. The following investment vehicles play a vital role:
Stocks
Investing in stocks provides ownership in companies and the potential for long-term growth. Key stock investment strategies include:
- Dividend Stocks: Generate passive income through regular dividend payments.
- Growth Stocks: Offer capital appreciation with high growth potential.
- Index Funds & ETFs: Provide diversification and lower risk.
Bonds
Bonds offer fixed income and are less volatile than stocks. Consider:
- Government Bonds: Safe but lower returns.
- Corporate Bonds: Higher yields with moderate risk.
- Municipal Bonds: Tax-advantaged income.
Real Estate
Investing in real estate generates rental income and appreciation in property value. Strategies include:
- Rental Properties: Buy properties to rent out for passive income.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Invest in real estate without direct ownership.
- House Flipping: Buy, renovate, and sell properties for profit.
Mutual Funds and ETFs
Mutual funds and ETFs allow investors to pool money and invest in diversified assets, reducing risk. They are ideal for beginners looking for professional management.
Alternative Investments
These include:
- Cryptocurrency: Digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Precious Metals: Gold and silver as hedges against inflation.
- Private Equity & Venture Capital: Investing in startups and businesses.

4. Diversifying Your Investment Portfolio
Diversification minimizes risk and stabilizes returns. Consider:
- Allocating funds across different asset classes.
- Investing in various industries and geographic regions.
- Balancing high-risk and low-risk investments.
5. Adopting a Long-Term Investment Strategy
Successful investing requires patience and discipline. Long-term strategies include:
- Buy and Hold: Holding investments for decades to capitalize on market growth.
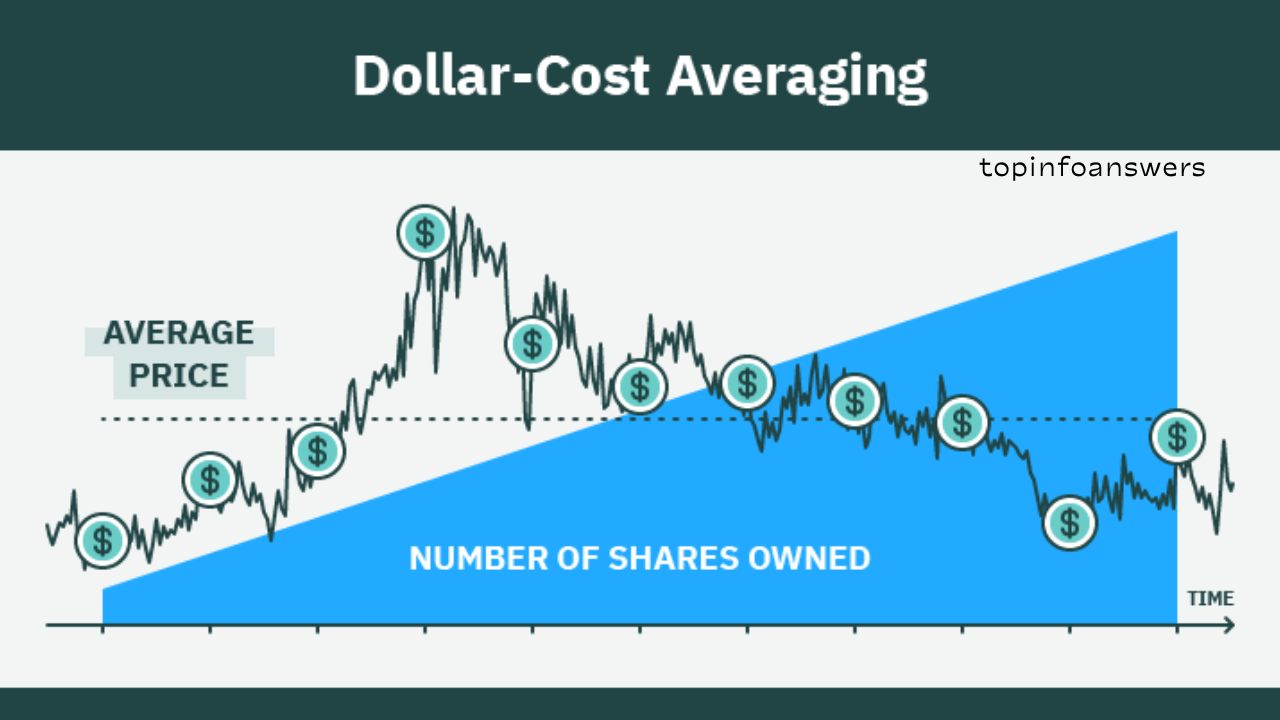
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Investing a fixed amount regularly, reducing market volatility impact.
- Compounding Interest: Reinvesting earnings for exponential growth.
6. Managing Investment Risks
Risk management protects your investments from losses. Essential risk management strategies include:
- Asset Allocation: Adjusting investments based on risk tolerance and time horizon.
- Emergency Fund: Keeping 3-6 months’ worth of expenses in liquid assets.
- Insurance: Protecting assets through health, life, and property insurance.
- Market Research: Staying informed about market trends and economic changes.
How to Plan Your Finances for Major Milestones (Marriage, Kids, etc.)
7. Generating Passive Income Streams
To achieve financial independence, focus on building passive income sources such as:
- Dividend Stocks: Companies that pay regular dividends.
- Real Estate Rentals: Properties generating monthly rent.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Earning interest from lending money.
- Online Businesses: Affiliate marketing, blogging, or digital products.
8. Tax Optimization Strategies
Smart investing involves reducing tax liabilities. Strategies include:
- Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Investing in 401(k), IRAs, or Roth IRAs.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: Selling underperforming assets to offset capital gains.
- Holding Periods: Avoiding short-term capital gains taxes by holding investments longer.

9. Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Investments
Markets change, and investment strategies should adapt accordingly. Steps to ensure optimal performance include:
- Annual Portfolio Review: Assess asset performance and reallocate if necessary.
- Adjusting to Life Changes: Modifying investments based on income changes, marriage, or retirement.
- Keeping Up with Financial Trends: Staying informed about emerging investment opportunities.
10. Seeking Professional Advice When Necessary
While self-investing is possible, professional guidance can enhance success. Consider:
- Financial Advisors: Personalized investment planning.
- Robo-Advisors: Automated investment management.
- Investment Courses & Books: Enhancing financial knowledge.
Achieving financial independence through smart investing requires discipline, education, and strategic planning. By setting financial goals, budgeting wisely, diversifying investments, and managing risks, individuals can build wealth and achieve financial security. The journey to financial independence is long-term but highly rewarding, providing financial freedom and security for the future.